Published: Nov 6, 2025 by Isaac Johnson
I had every intention of just doing a quick test of UpCloud. I already knew of them by way of Aiven.io which offers some services backed by UpCloud.
But the more I dug in, the more I found myself really enjoying UpCloud. Fewer and fewer cloud providers really give a decent trial and 7days/$10 covers a lot of ground if you move fast. I think everything you see in the next two articles was under US$2 in spend and just a day or two in time.
Let’s start with setup
UpCloud Setup
I’ll start a free trial from their signup page.
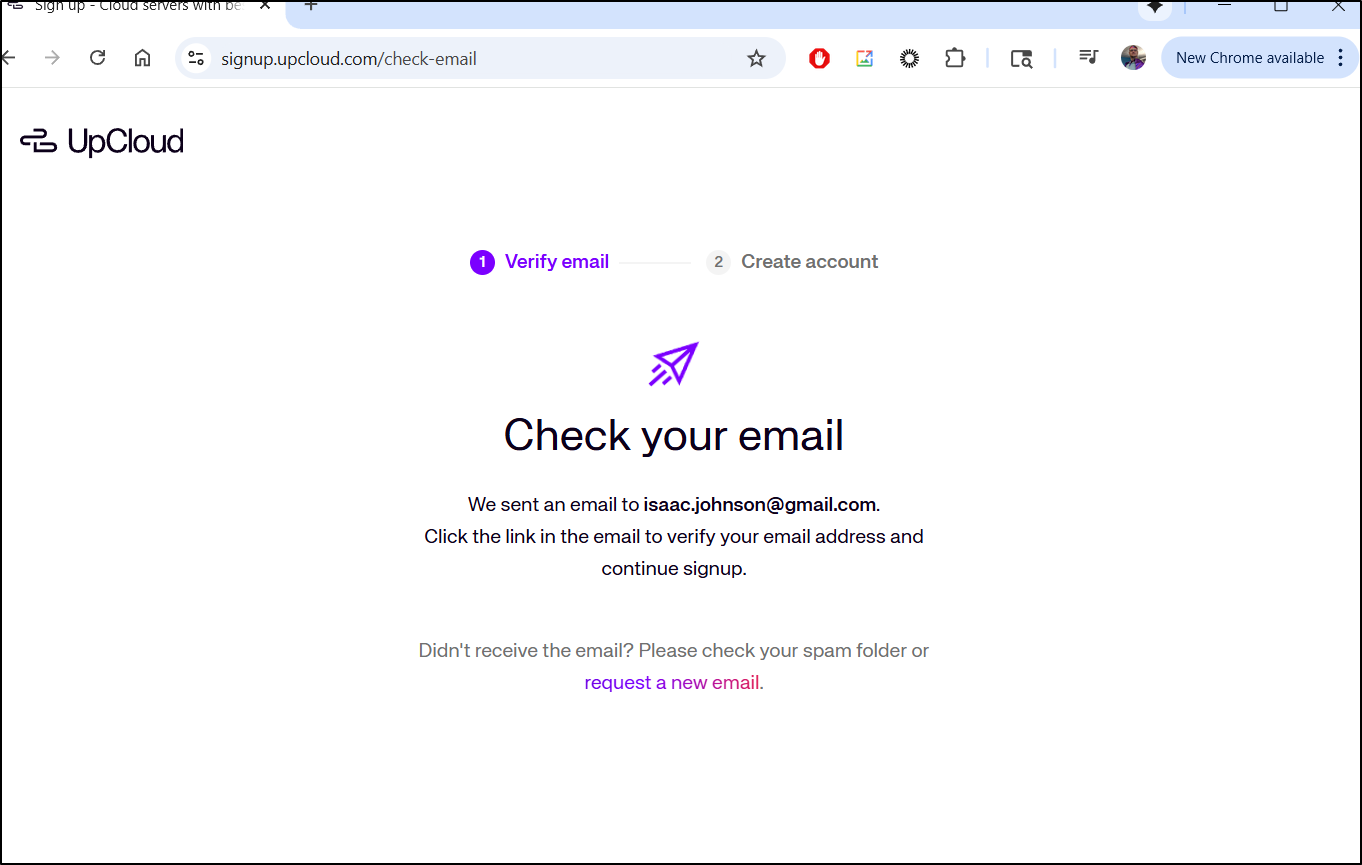
I need to verify my email
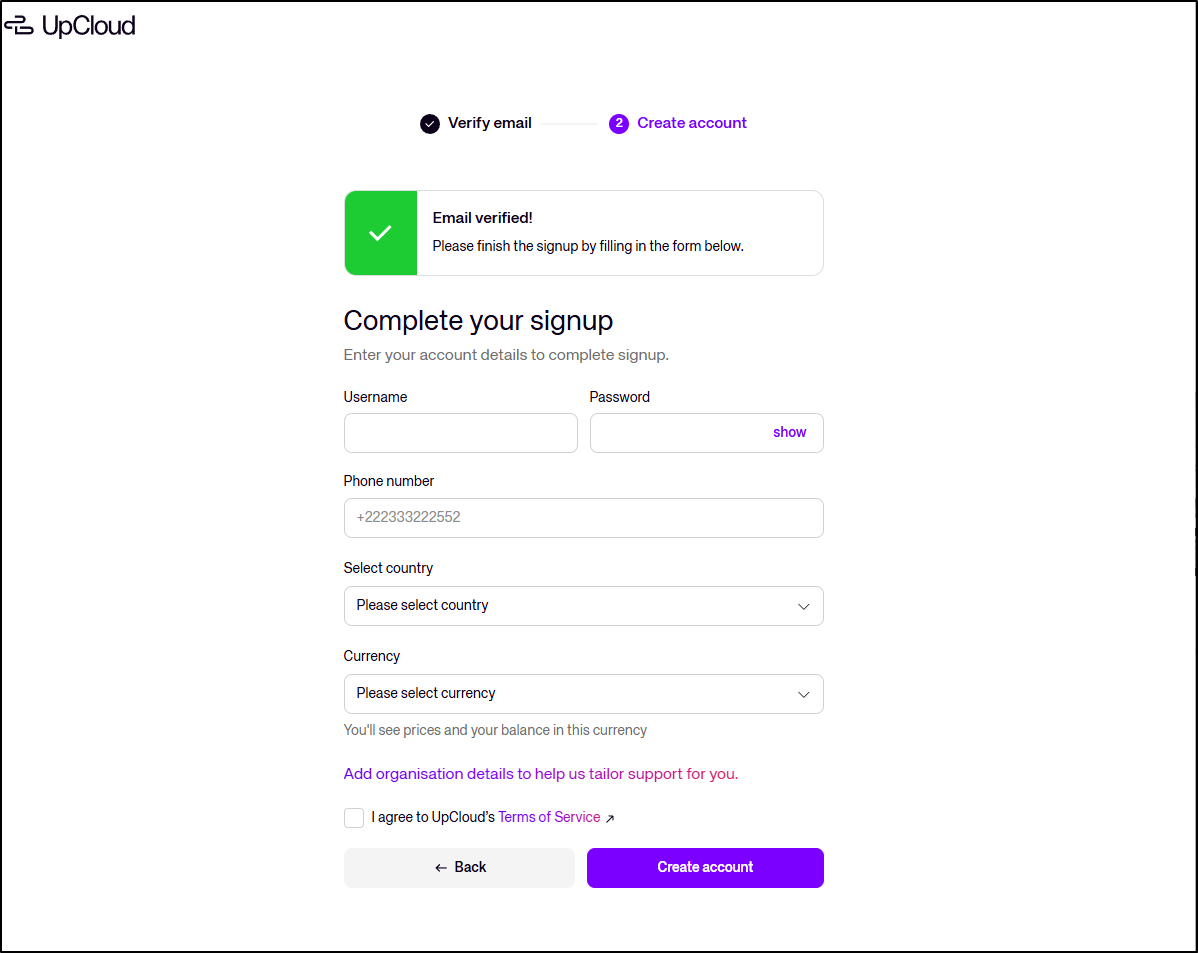
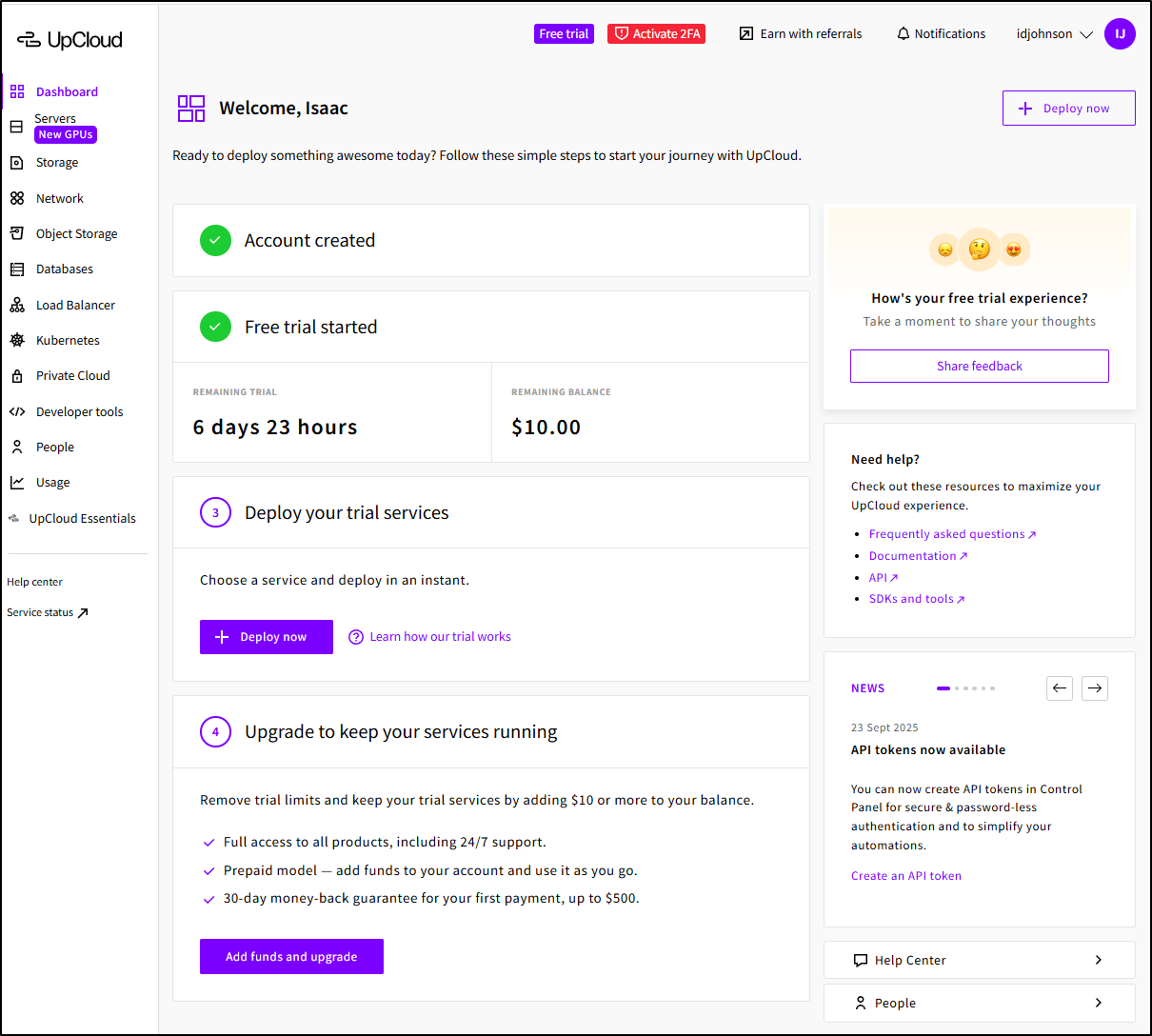
Then I can setup some account details
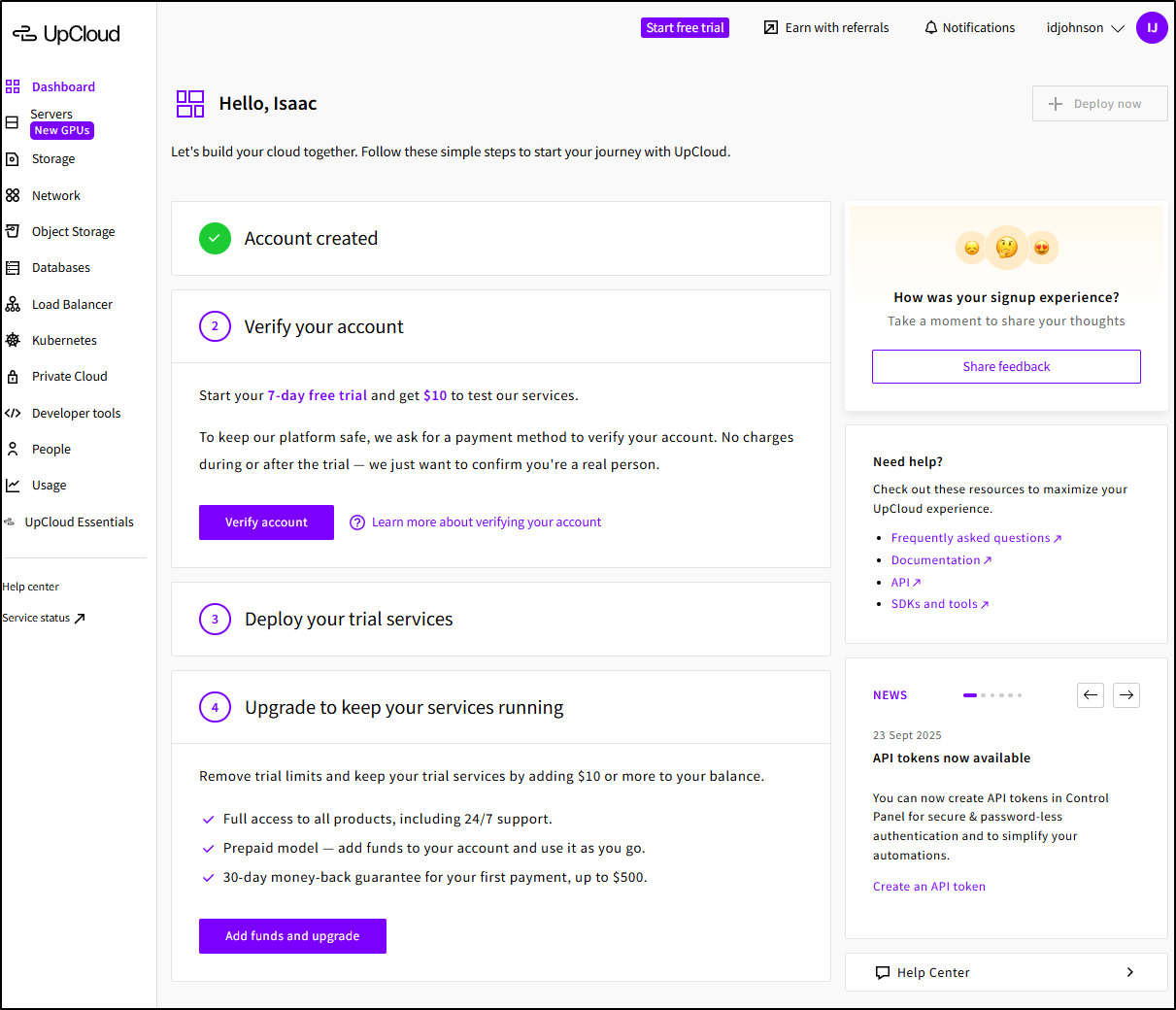
Now that I’m signed up I have $10 and 7days to mess about which is more than enough (IMHO).
Now, to get those credits, we need to verify our account (by using a credit card). I accept these terms.
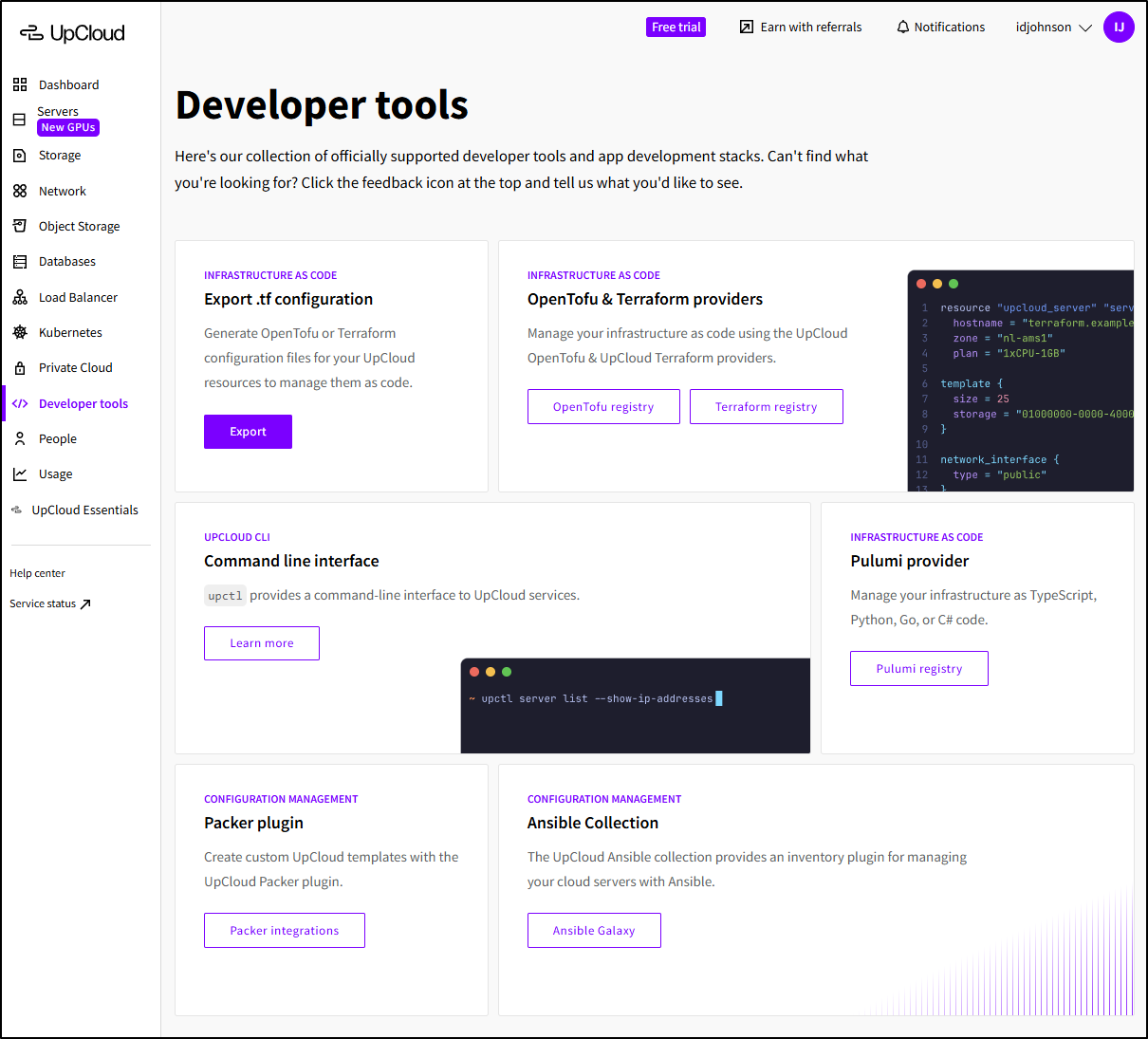
I was about to create a server when I noticed the Developer tools section:
This is nice. These people get me.
Let’s start with the CLI
CLI usage
The install page gives us options for Linux, macOS, Windows, golang, Docker, mise, aqua and AUR.
I’ll use the apt option for my local Ubuntu
$ curl -Lo upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb https://github.com/UpCloudLtd/upcloud-cli/releases/download/v3.25.0/upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
100 18.6M 100 18.6M 0 0 18.3M 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 18.3M
$ sudo apt install ./upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb
[sudo] password for builder:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
Note, selecting 'upcloud-cli' instead of './upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb'
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
aspnetcore-runtime-3.1 aspnetcore-targeting-pack-3.1 aspnetcore-targeting-pack-6.0 crda cryptsetup-run
dotnet-apphost-pack-3.1 dotnet-apphost-pack-6.0 dotnet-runtime-deps-6.0 dotnet-runtime-deps-8.0
dotnet-targeting-pack-3.1 dotnet-targeting-pack-6.0 fluent-bit g++-9 gcc-10-base gir1.2-gnomebluetooth-1.0
gjs golang-1.13 golang-1.13-doc golang-1.13-go golang-1.13-race-detector-runtime golang-1.13-src
golang-race-detector-runtime i965-va-driver:i386 intel-media-va-driver:i386 ippusbxd libaom0 libaom0:i386
libaom3:i386 libappstream-glib8 libasn1-8-heimdal libasn1-8-heimdal:i386 libasync-mergepoint-perl
libavcodec58:i386 libavutil56:i386 libboost-context1.71.0 libboost-iostreams1.71.0
libboost-program-options1.71.0 libboost-thread1.71.0 libcamel-1.2-62 libcbor0.6 libcdio18 libcodec2-0.9
libcodec2-0.9:i386 libcodec2-1.0:i386 libcroco3 libcurl3-gnutls:i386 libdav1d5:i386 libdbus-glib-1-2
libdc1394-22 libdigest-bubblebabble-perl libdns-export1109 libedataserver-1.2-24 libedataserverui-1.2-2
libemail-valid-perl libevent-2.1-7 libffi7:i386 libfl2 libfuture-perl libfwupdplugin1 libgdbm-compat4:i386
libgdbm6:i386 libgdk-pixbuf-xlib-2.0-0:i386 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0:i386 libgetopt-long-descriptive-perl
libglu1-mesa libglu1-mesa:i386 libgomp1:i386 libgssapi3-heimdal libgssapi3-heimdal:i386 libgupnp-1.2-0
libhcrypto4-heimdal libhcrypto4-heimdal:i386 libheimbase1-heimdal libheimbase1-heimdal:i386
libheimntlm0-heimdal libheimntlm0-heimdal:i386 libhiredis0.14 libhogweed5 libhogweed5:i386
libhx509-5-heimdal libhx509-5-heimdal:i386 libicu66:i386 libidn11 libieee1284-3:i386 libigdgmm11
libigdgmm11:i386 libigdgmm12:i386 libilmbase24 libio-async-loop-epoll-perl libio-async-perl libjson-c4
libjsoncpp1 libkrb5-26-heimdal libkrb5-26-heimdal:i386 libldap-2.4-2 libldap-2.4-2:i386 libleveldb1d
liblinux-epoll-perl libllvm12 libllvm12:i386 liblttng-ust-ctl4 liblttng-ust0 liblua5.2-0
libmetrics-any-perl libmozjs-68-0 libmpdec2 libmysqlclient21:i386 libnet-dns-perl libnet-dns-sec-perl
libnet-ip-perl libnettle7 libnettle7:i386 libnspr4:i386 libnss3:i386 libntfs-3g883 libnuma1:i386
libnumber-range-perl libodbc1 libopenexr24 libopengl0:i386 libopenjp2-7:i386 libparams-validate-perl
libpci3:i386 libperl4-corelibs-perl libperl5.30 libperl5.30:i386 libperl5.34:i386 libpgm-5.2-0
libphonenumber7 libpoppler-glib8:i386 libpoppler118:i386 libprotobuf17 libpython2-stdlib
libpython2.7-minimal libpython2.7-stdlib libpython3.8 libpython3.8-dev libpython3.8-minimal
libpython3.8-stdlib libre2-5 libreadline5 libroken18-heimdal libroken18-heimdal:i386 librsvg2-2:i386
librsvg2-common:i386 libsane libsane:i386 libsane1:i386 libsereal-perl libshine3:i386 libsnappy1v5:i386
libsnmp35 libsnmp35:i386 libsnmp40:i386 libsort-key-perl libsoxr0:i386 libssl1.1:i386 libstdc++-9-dev
libstruct-dumb-perl libswresample3:i386 libtest-fatal-perl libtest-metrics-any-perl libtest-refcount-perl
libtext-levenshtein-perl liburcu6 libva-drm2:i386 libva-x11-2:i386 libva2:i386 libvdpau1:i386 libvpx6
libvpx6:i386 libwebp6 libwebp6:i386 libwebpmux3:i386 libwind0-heimdal libwind0-heimdal:i386 libwmf-0.2-7
libwmf0.2-7 libwrap0:i386 libx264-155 libx264-155:i386 libx264-163:i386 libx265-179 libx265-179:i386
libx265-199:i386 libxml-writer-perl libxmlb1 libxvidcore4:i386 libzvbi0:i386 linux-headers-5.15.0-152
linux-headers-5.15.0-152-generic linux-headers-5.4.0-208 linux-headers-5.4.0-208-generic
linux-headers-5.4.0-216 linux-headers-5.4.0-216-generic ltrace lz4 mariadb-common mesa-va-drivers:i386
mesa-vdpau-drivers:i386 mousetweaks perl-modules-5.30 popularity-contest python-pkg-resources python2
python2-minimal python2.7 python2.7-minimal python3-crcmod python3-entrypoints python3-requests-unixsocket
python3-simplejson python3.8 python3.8-dev python3.8-minimal ruby-afm ruby-ascii85 ruby-blankslate
ruby-connection-pool ruby-hashery ruby-launchy-shim ruby-molinillo ruby-multi-json ruby-net-http-persistent
ruby-oj ruby-parslet ruby-pdf-core ruby-pdf-reader ruby-posix-spawn ruby-prawn ruby-prawn-table ruby-rc4
ruby-stringex ruby-thor ruby-toml ruby-ttfunk ruby2.7 ruby2.7-dev ruby2.7-doc td-agent-bit
va-driver-all:i386 vdpau-driver-all:i386 x11proto-input-dev x11proto-randr-dev x11proto-xinerama-dev
xul-ext-ubufox
Use 'sudo apt autoremove' to remove them.
The following NEW packages will be installed:
upcloud-cli
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 1 not upgraded.
Need to get 0 B/19.6 MB of archives.
After this operation, 64.1 MB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 /home/builder/Workspaces/jekyll-blog/upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb upcloud-cli amd64 3.25.0 [19.6 MB]
Selecting previously unselected package upcloud-cli.
(Reading database ... 403462 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../upcloud-cli_3.25.0_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking upcloud-cli (3.25.0) ...
Setting up upcloud-cli (3.25.0) ...
Scanning processes...
Scanning processor microcode...
Scanning linux images...
Failed to retrieve available kernel versions.
The processor microcode seems to be up-to-date.
No services need to be restarted.
No containers need to be restarted.
No user sessions are running outdated binaries.
No VM guests are running outdated hypervisor (qemu) binaries on this host.
I can now see the version respond
$ upctl version
Version: 3.25.0
Build date: 2025-10-24T09:20:29Z
Built with: go1.25.3
System: linux
Architecture: amd64
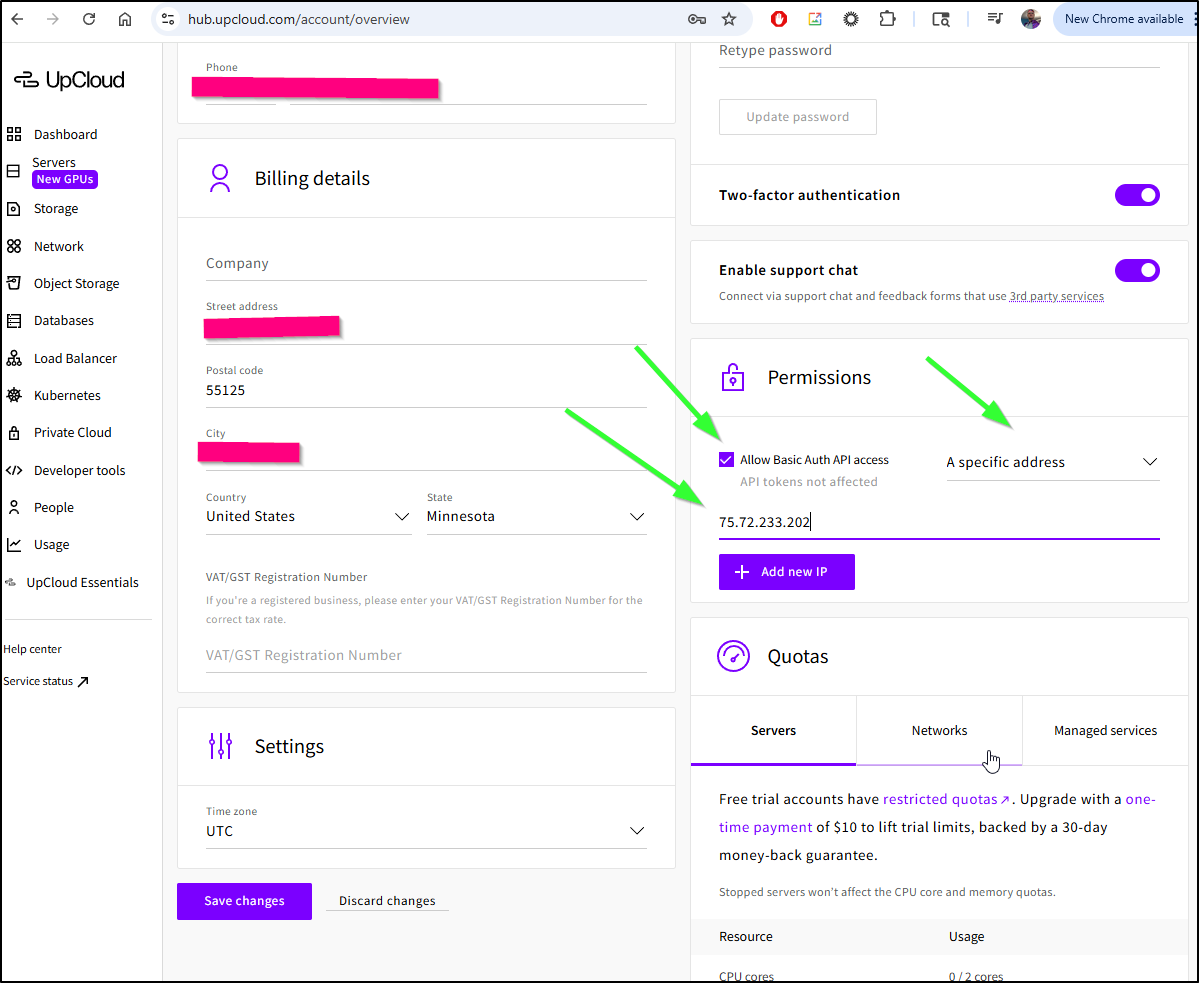
I found that even if I entered creds, by default it blocks all traffic
$ export UPCLOUD_USERNAME=idjohnson
$ export UPCLOUD_PASSWORD='xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
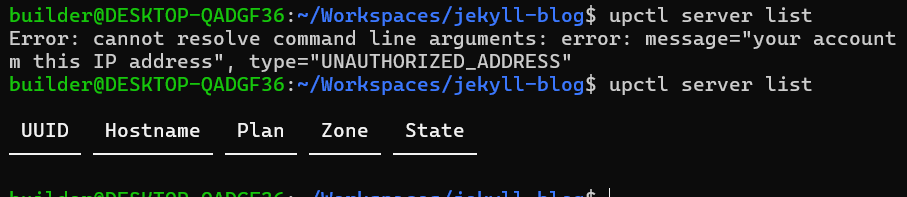
$ upctl server list
Error: cannot resolve command line arguments: error: message="your account is not allowed to access the API from this IP address", type="UNAUTHORIZED_ADDRESS"
Let’s add our external IP address
$ dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com
75.72.233.202
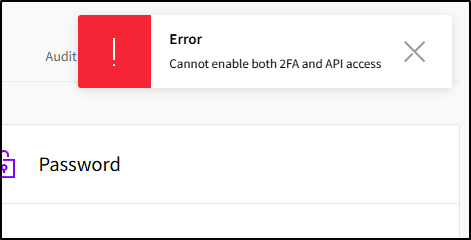
I was a bit bummed I have to disable MFA to enable API access
Now this works
Let’s create a server and use our local SSH keys
$ upctl server create --wait --title myapp --zone fi-hel1 --hostname myapp --ssh-keys ~/.ssh/id_*.pub --plan 2xCPU-4GB
✓ Creating server myapp 62 s
UUID 00e453cb-de6c-4f57-ab5d-6ccaf4f314ad
IP Addresses 94.237.119.82,
10.1.15.53,
2a04:3540:1000:310:70c6:75ff:fedc:10db
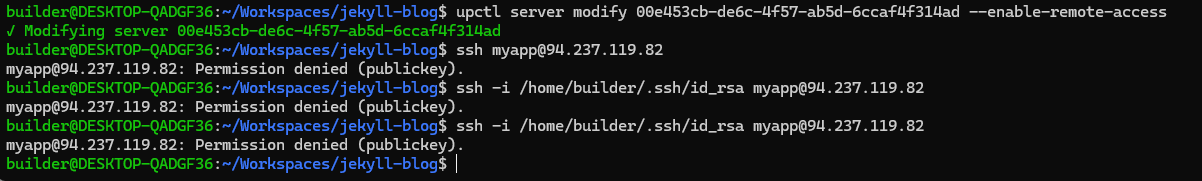
I tried a few ways to login, but none seemed to work
I even tried a simple restart
However, when I deleted this instance and tried again, this time giving it the explicit SSH key and admin username:
$ upctl server create --wait --title myapp --zone fi-hel1 --hostname myapp --ssh-keys /home/builder/.ssh/id_rsa.pub --username admin --plan 2xCPU-4GB
✓ Creating server myapp 65 s
UUID 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
IP Addresses 10.1.15.53,
2a04:3540:1000:310:70c6:75ff:fedc:239e,
94.237.116.240
Then it worked
$ ssh -i /home/builder/.ssh/id_rsa admin@94.237.116.240
The authenticity of host '94.237.116.240 (94.237.116.240)' can't be established.
ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:qia7f9A4PREya2oRQ9LXK5PUKtyI/J+nEgAPCMQDMKQ.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
Warning: Permanently added '94.237.116.240' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts.
Welcome to Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.8.0-63-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/pro
System information as of Sat Oct 25 08:49:15 PM UTC 2025
System load: 0.37
Usage of /: 3.1% of 78.68GB
Memory usage: 6%
Swap usage: 0%
Processes: 110
Users logged in: 0
IPv4 address for eth0: 94.237.116.240
IPv6 address for eth2: 2a04:3540:1000:310:70c6:75ff:fedc:239e
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates.
See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status
The list of available updates is more than a week old.
To check for new updates run: sudo apt update
The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by
applicable law.
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
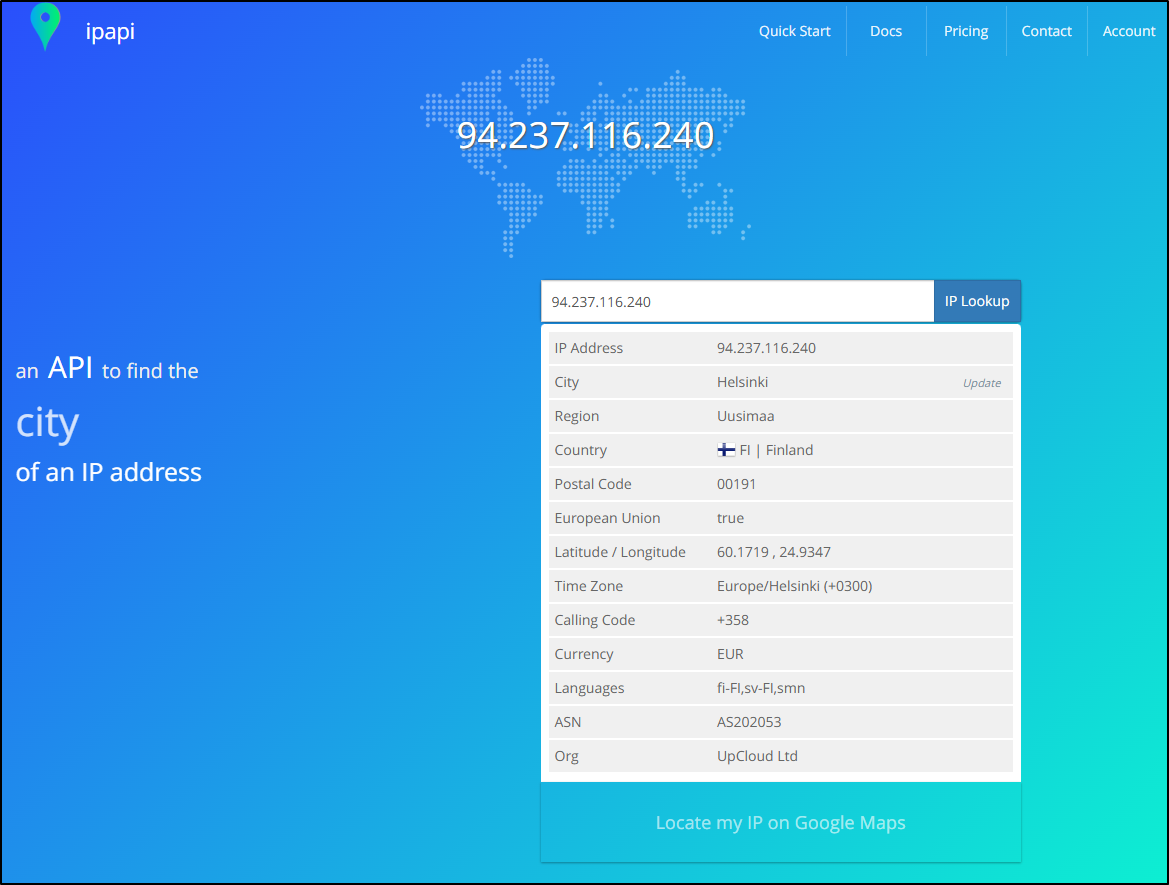
It doesn’t say explicitly where this server is located, but a quick check with ipapi suggests it is indeed in Finland
This server is so fast. I am envious the internet other places get.
This time I’ll stop it and delete from the CLI
$ upctl server list
UUID Hostname Plan Zone State
────────────────────────────────────── ────────── ─────────── ───────── ─────────
005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876 myapp 2xCPU-4GB fi-hel1 started
$ upctl server stop 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
✓ Stopping server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
$ upctl server delete 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
✗ Deleting server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
Error: error: message="The operation is not allowed while the server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876 is in
state 'maintenance'.", type="SERVER_STATE_ILLEGAL"
Error: Command execution failed for 1 resource(s)
$ upctl server delete 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
✗ Deleting server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
Error: error: message="The operation is not allowed while the server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876 is in
state 'maintenance'.", type="SERVER_STATE_ILLEGAL"
Error: Command execution failed for 1 resource(s)
$ upctl server list
UUID Hostname Plan Zone State
────────────────────────────────────── ────────── ─────────── ───────── ─────────
005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876 myapp 2xCPU-4GB fi-hel1 stopped
$ upctl server delete 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
✓ Deleting server 005b29cd-2962-4e92-a86b-6201d5ffe876
UpCloud hub
I showed using the upctl CLI. Now let’s do the same thing with the Hub.
We’ll go to Servers/Cloud Servers and click “+ Deploy server”
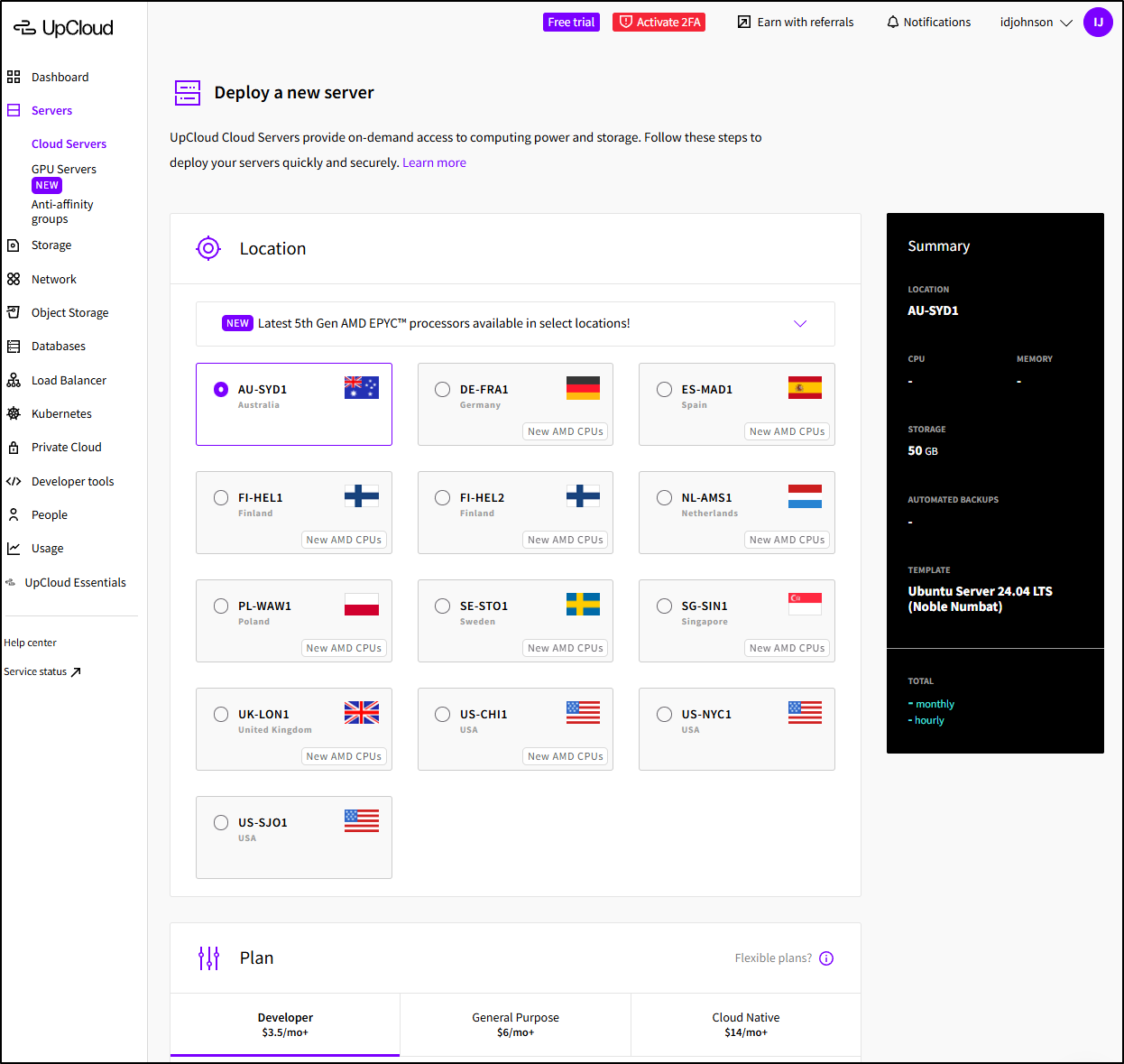
I can then pick the location (I dig the little flags)
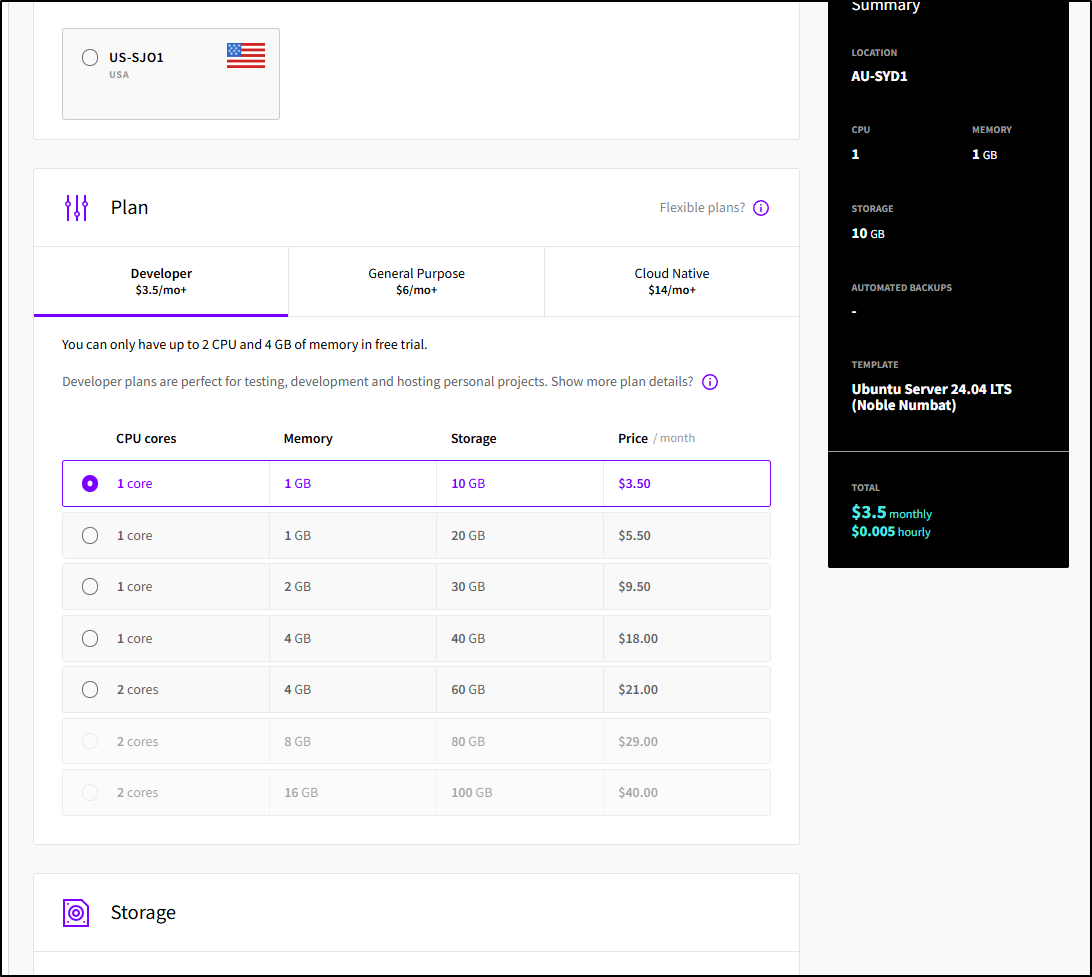
Then the plan which went as low as 1cpu/10Gb
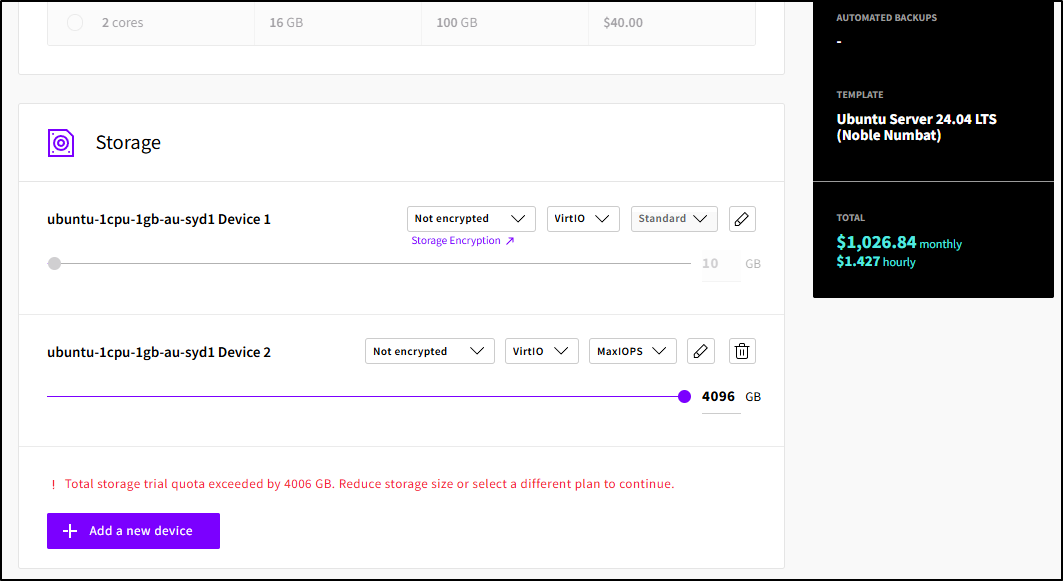
The primary OS disk is fixed (other than I can rename it). I can, however, add another volume up to 4Tb
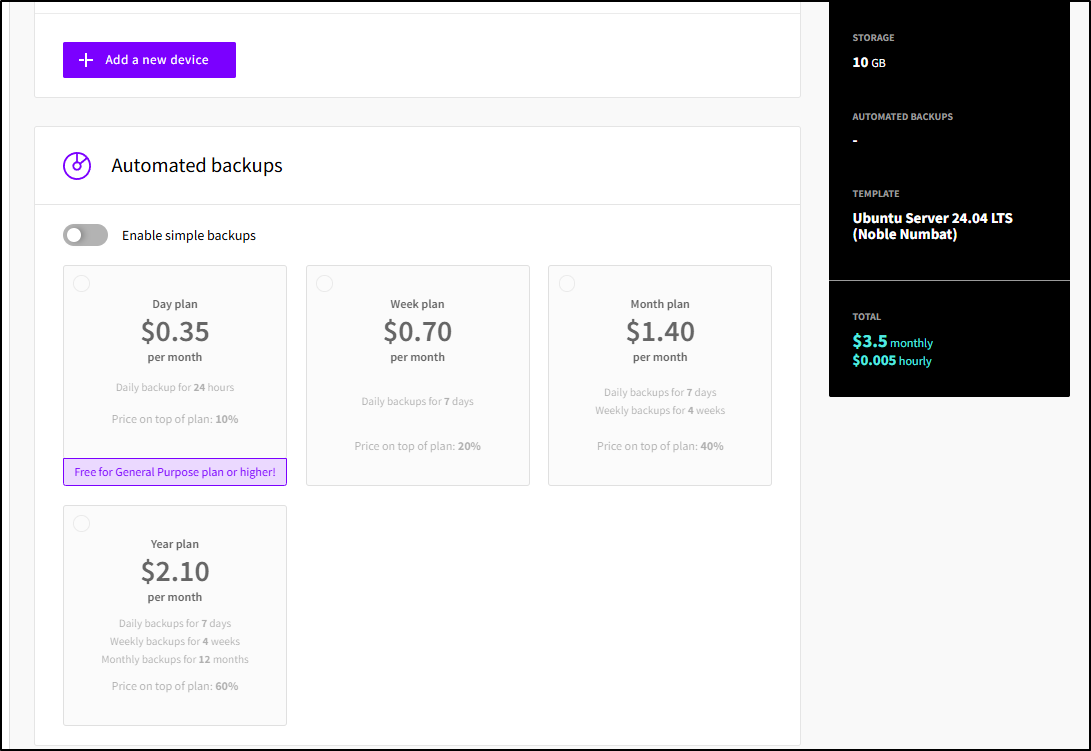
with GCP and Azure, we need to make a backup plan either during or after instance creation. With UpCloud, they have a nice simple “Automated Backups” option we can use. The daily backup is included at the GP plan and higher
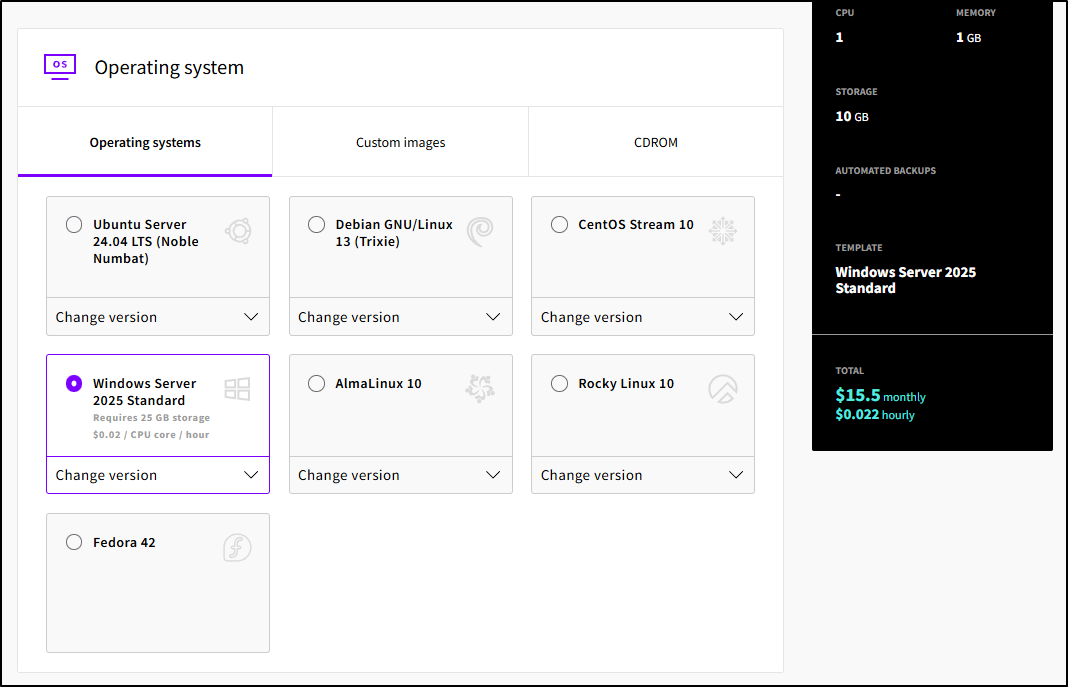
As for OS options, they have a bunch of options including Ubuntu, Cent and Windows Server. Though Windows will jump the price 2c per core per hour
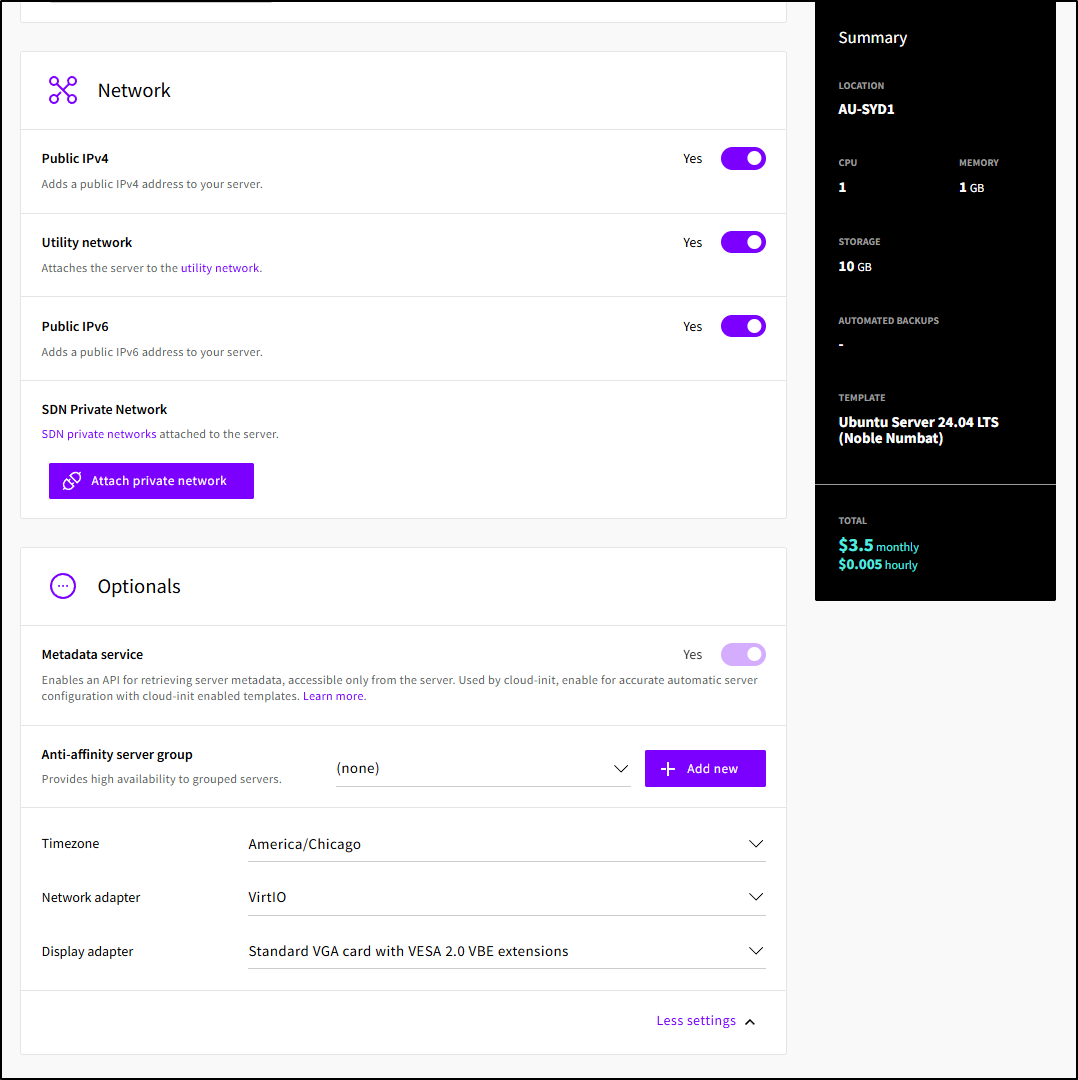
We can choose whether to add a Public IP and optionally set the Timezone (Default is UTC)
If we do SSH keys, we need to paste in our public key (typically ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
Lastly, we can set an init script and number of instances. I’m going to try and use the linux installer script for Azure CLI as an init script here.
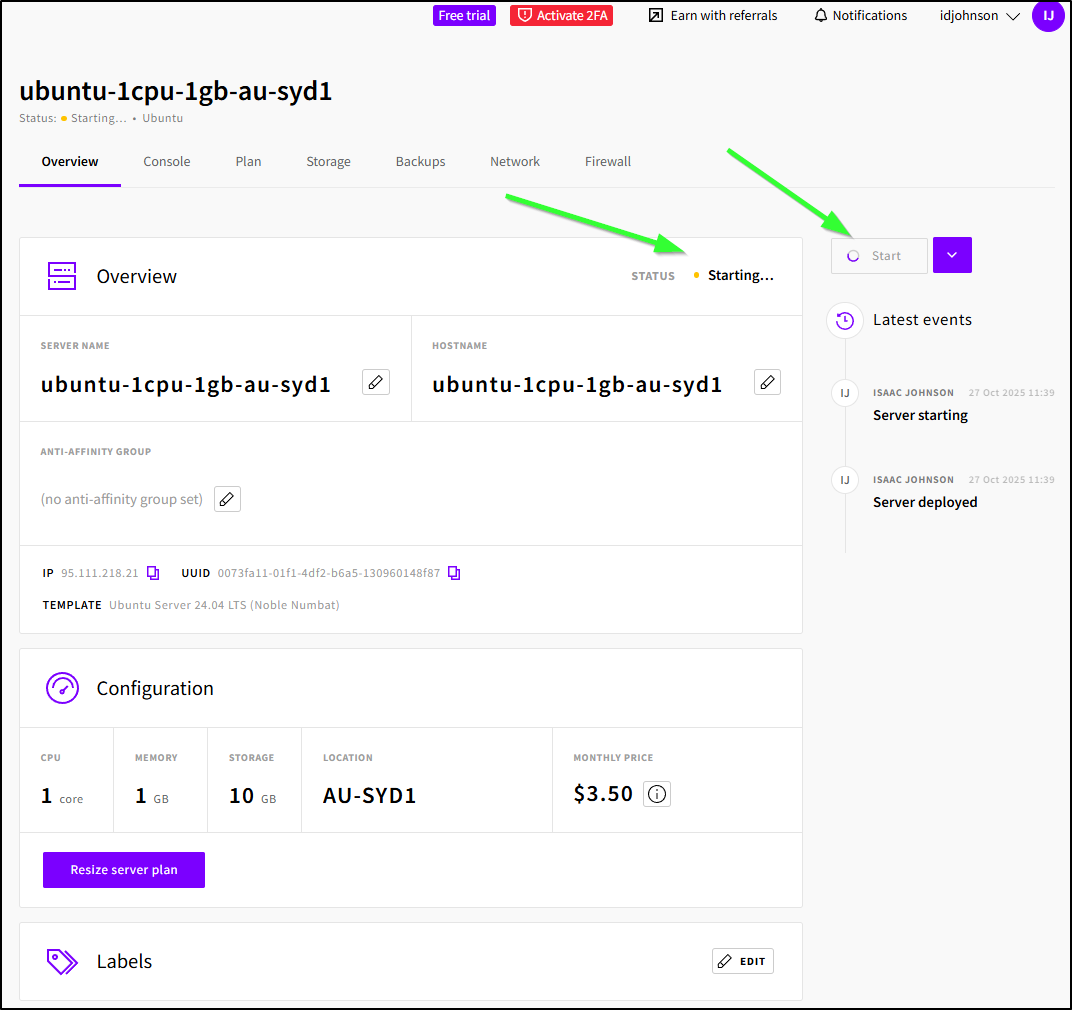
Once I click Deploy, I can see it starting up in the Hub
If we click the instance, we can also see that it is “Starting”
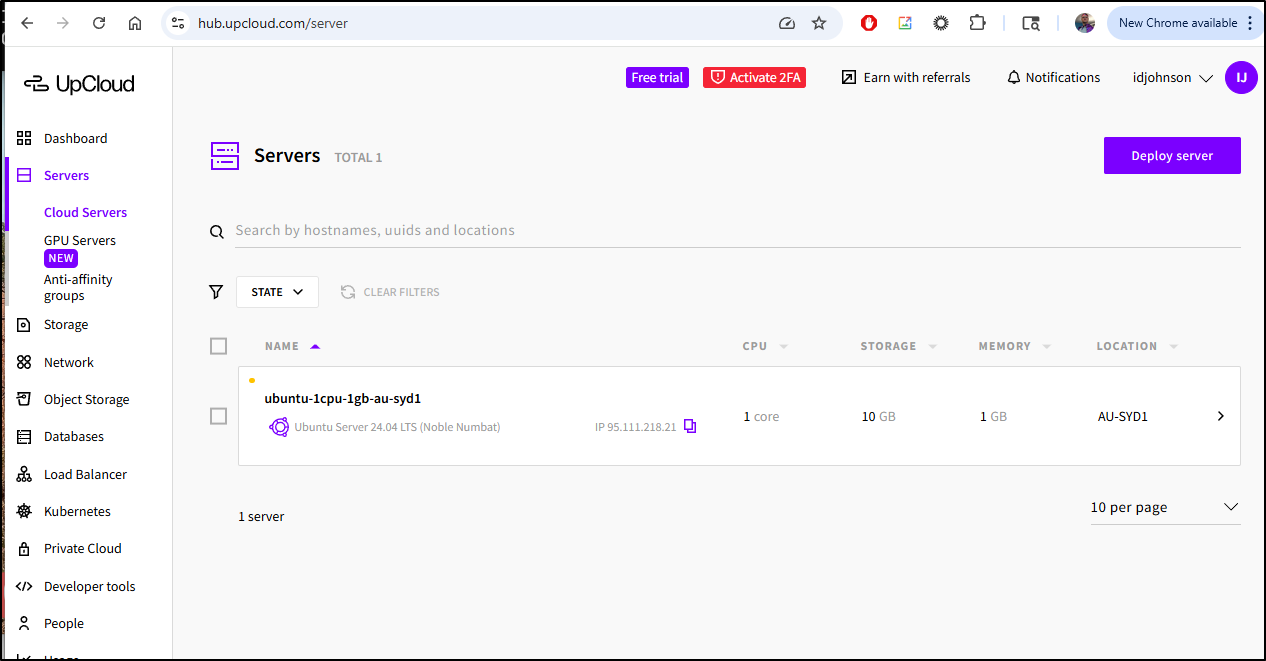
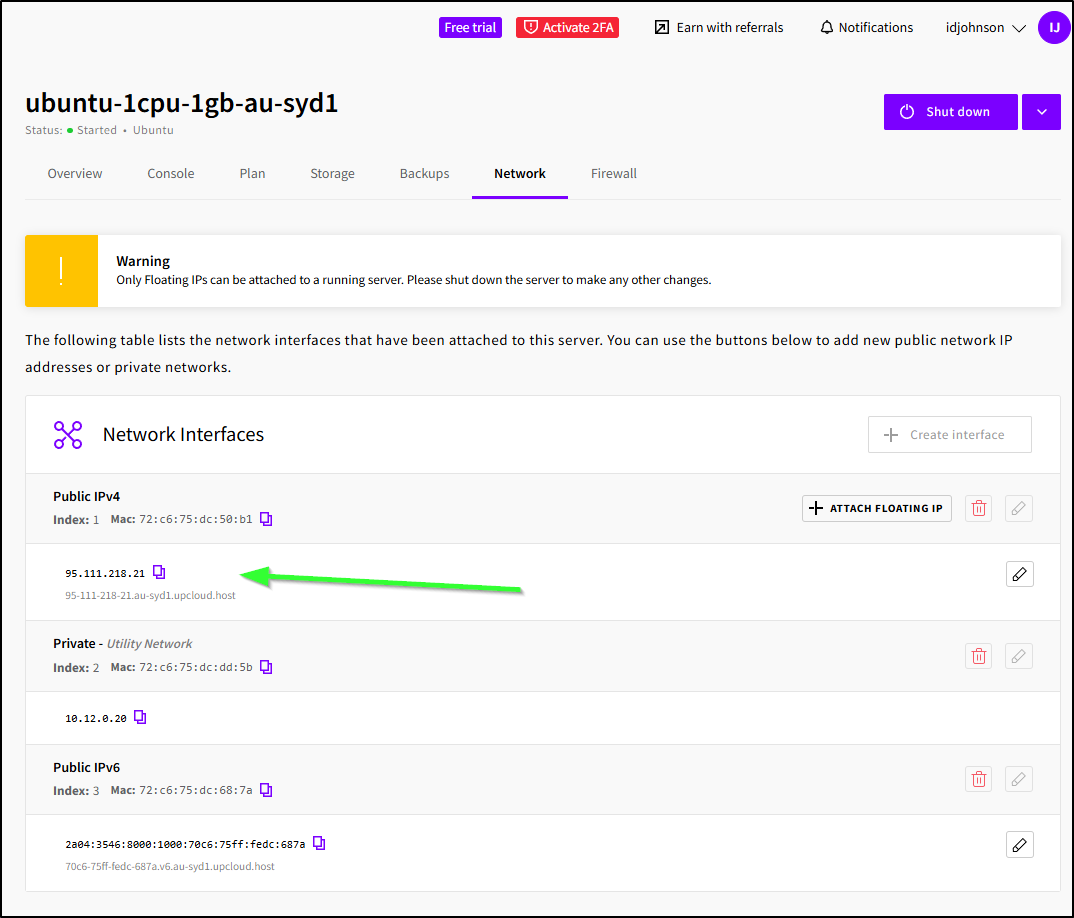
Once started, we can look at the Network Interfaces to see the public IP
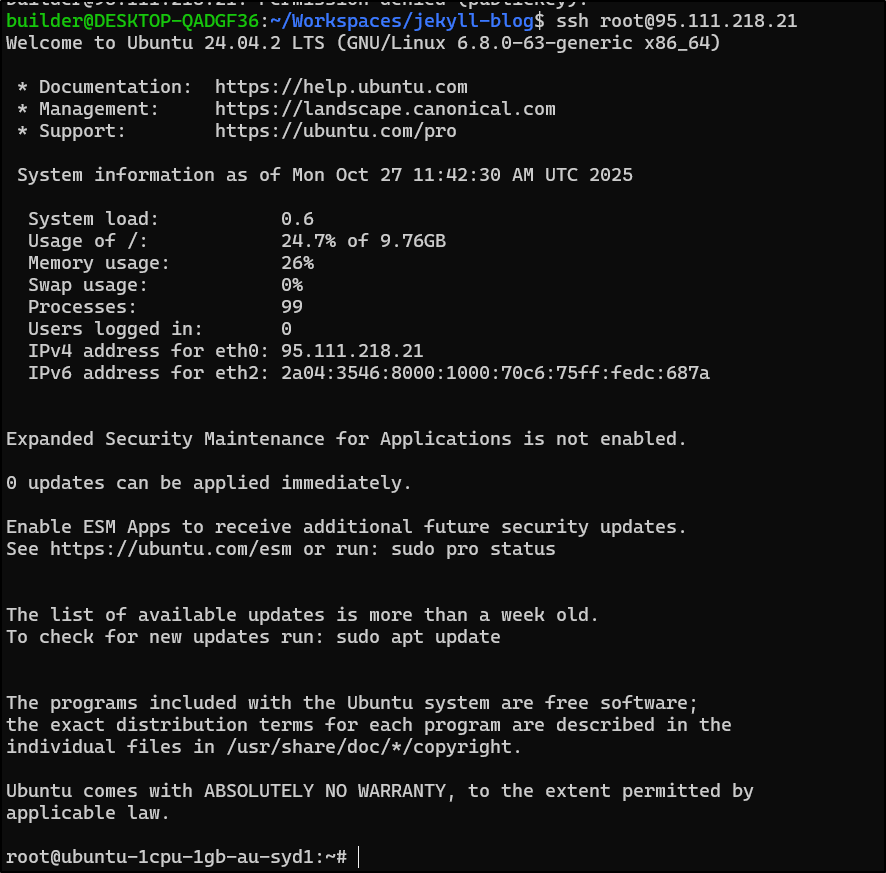
To SSH from a console, make sure to seek “root” access if you didn’t override the admin user
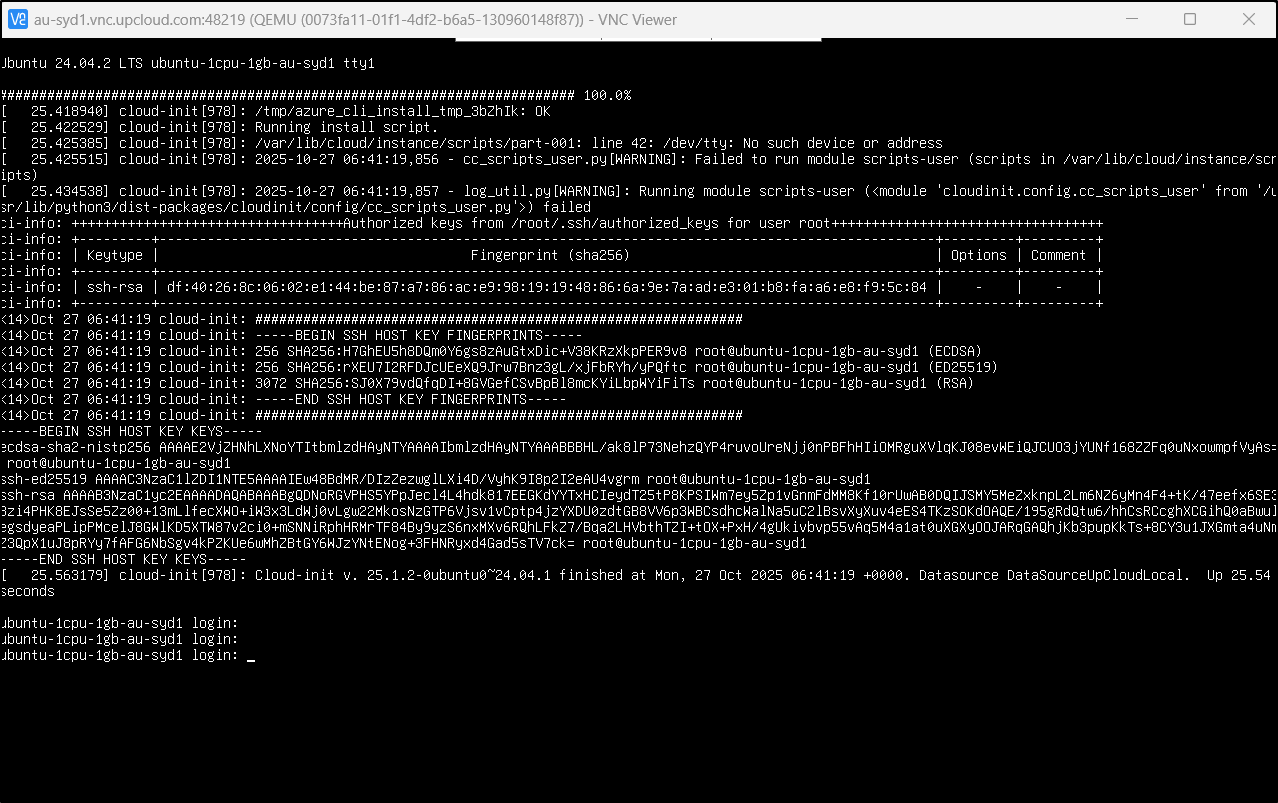
I didn’t see the az command so I checked the cloud-init logs for errors
root@ubuntu-1cpu-1gb-au-syd1:~# cat /var/log/cloud-init.log
2025-10-27 06:41:04,634 - log_util.py[DEBUG]: Cloud-init v. 25.1.2-0ubuntu0~24.04.1 running 'init-local' at Mon, 27 Oct 2025 06:41:04 +0000. Up 10.17 seconds.
2025-10-27 06:41:04,634 - main.py[INFO]: PID [1] started cloud-init 'init-local'.
2025-10-27 06:41:04,634 - main.py[DEBUG]: No kernel command line url found.
2025-10-27 06:41:04,634 - main.py[DEBUG]: Closing stdin
2025-10-27 06:41:04,746 - util.py[DEBUG]: Writing to /var/log/cloud-init.log - ab: [640] 0 bytes
2025-10-27 06:41:04,747 - util.py[DEBUG]: Changing the ownership of /var/log/cloud-init.log to 103:4
2025-10-27 06:41:04,747 - util.py[DEBUG]: Writing to /var/lib/cloud/data/python-version - wb: [644] 4 bytes
2025-10-27 06:41:04,747 - util.py[DEBUG]: Attempting to remove /var/lib/cloud/instance/boot-finished
2025-10-27 06:41:04,748 - handlers.py[DEBUG]: start: init-local/check-cache: attempting to read from cache [check]
2025-10-27 06:41:04,748 - util.py[DEBUG]: Reading from /var/lib/cloud/instance/obj.pkl (quiet=False)
2025-10-27 06:41:04,748 - stages.py[DEBUG]: no cache found
2025-10-27 06:41:04,748 - handlers.py[DEBUG]: finish: init-local/check-cache: SUCCESS: no cache found
2025-10-27 06:41:04,751 - stages.py[DEBUG]: Using distro class <class 'cloudinit.distros.ubuntu.Distro'>
2025-10-27 06:41:04,751 - sources[DEBUG]: Looking for data source in: ['UpCloud', 'None'], via packages ['', 'cloudinit.sources'] that matches dependencies ['FILESYSTEM']
... snip ...
2025-10-27 06:41:19,856 - subp.py[DEBUG]: Unexpected error while running command.
Command: ['/var/lib/cloud/instance/scripts/part-001']
Exit code: 1
Reason: -
Stdout: -
Stderr: -
2025-10-27 06:41:19,856 - cc_scripts_user.py[WARNING]: Failed to run module scripts-user (scripts in /var/lib/cloud/instance/scripts)
2025-10-27 06:41:19,857 - handlers.py[DEBUG]: finish: modules-final/config-scripts-user: FAIL: running config-scripts-user with frequency once-per-instance
2025-10-27 06:41:19,857 - log_util.py[WARNING]: Running module scripts-user (<module 'cloudinit.config.cc_scripts_user' from '/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/config/cc_scripts_user.py'>) failed
2025-10-27 06:41:19,865 - log_util.py[DEBUG]: Running module scripts-user (<module 'cloudinit.config.cc_scripts_user' from '/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/config/cc_scripts_user.py'>) failed
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/config/modules.py", line 297, in _run_modules
ran, _r = cc.run(
^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/cloud.py", line 71, in run
return self._runners.run(name, functor, args, freq, clear_on_fail)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/helpers.py", line 156, in run
results = functor(**args)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/config/cc_scripts_user.py", line 38, in handle
subp.runparts(runparts_path)
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/subp.py", line 387, in runparts
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: Runparts: 1 failures (part-001) in 1 attempted commands
2025-10-27 06:41:19,876 - modules.py[DEBUG]: Running module ssh-authkey-fingerprints (<module 'cloudinit.config.cc_ssh_authkey_fingerprints' from '/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/cloudinit/config/cc_ssh_authkey_fingerprints.py'>) with frequency once-per-instance
2025-10-27 06:41:19,876 - handlers.py[DEBUG]: start: modules-final/config-ssh-authkey-fingerprints: running config-ssh-authkey-fingerprints with frequency once-per-instance
... snip ...
seems (from Stack Overflow) it is likely timeouts or apt locks being held.
At least I know it tried. I tried directly and it seems this linux command was requiring interactive.
root@ubuntu-1cpu-1gb-au-syd1:~# curl -L https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCli | bash
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
100 1405 100 1405 0 0 1078 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 1078
Downloading Azure CLI install script from https://azurecliprod.blob.core.windows.net/install.py to /tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT.
######################################################################## 100.0%
/tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT: OK
Running install script.
-- Verifying Python version.
-- Python version 3.12.3 okay.
-- Verifying native dependencies.
-- Unable to verify native dependencies. dist=ubuntu, version=24.04. Continuing...
===> In what directory would you like to place the install? (leave blank to use '/root/lib/azure-cli'):
-- Creating directory '/root/lib/azure-cli'.
-- We will install at '/root/lib/azure-cli'.
===> In what directory would you like to place the 'az' executable? (leave blank to use '/root/bin'):
-- Creating directory '/root/bin'.
-- The executable will be in '/root/bin'.
-- Downloading virtualenv package from https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/v/virtualenv/virtualenv-16.7.11.tar.gz.
-- Downloaded virtualenv package to /tmp/tmp4lz56tbx/virtualenv-16.7.11.tar.gz.
-- Checksum of /tmp/tmp4lz56tbx/virtualenv-16.7.11.tar.gz OK.
-- Extracting '/tmp/tmp4lz56tbx/virtualenv-16.7.11.tar.gz' to '/tmp/tmp4lz56tbx'.
-- Executing: ['/usr/bin/python3', 'virtualenv.py', '--python', '/usr/bin/python3', '/root/lib/azure-cli']
Already using interpreter /usr/bin/python3
Using base prefix '/usr'
New python executable in /root/lib/azure-cli/bin/python3
Also creating executable in /root/lib/azure-cli/bin/python
ERROR: The executable /root/lib/azure-cli/bin/python3 is not functioning
ERROR: It thinks sys.prefix is '/usr' (should be '/root/lib/azure-cli')
ERROR: virtualenv is not compatible with this system or executable
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT", line 415, in <module>
main()
File "/tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT", line 399, in main
create_virtualenv(tmp_dir, install_dir)
File "/tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT", line 144, in create_virtualenv
exec_command(cmd, cwd=working_dir)
File "/tmp/azure_cli_install_tmp_gRIDiT", line 105, in exec_command
subprocess.check_call(command_list, cwd=cwd, env=env)
File "/usr/lib/python3.12/subprocess.py", line 413, in check_call
raise CalledProcessError(retcode, cmd)
subprocess.CalledProcessError: Command '['/usr/bin/python3', 'virtualenv.py', '--python', '/usr/bin/python3', '/root/lib/azure-cli']' returned non-zero exit status 100.
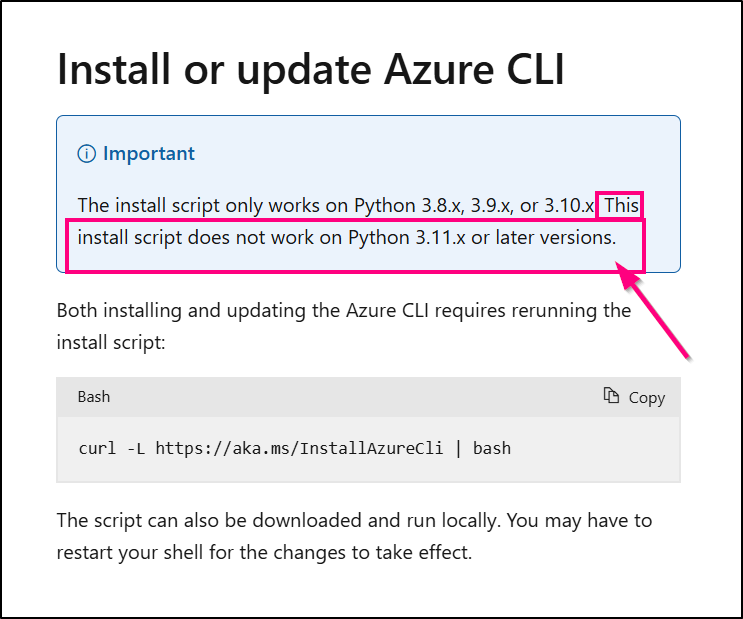
Also, the Ubuntu is the latest Noble. I’m guessing our Python version is too new for the install script (now that I double check the documentation)
However, I was able to install the Azure CLI with
$ curl -sL https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | sudo bash
A quick check on version:
root@ubuntu-1cpu-1gb-au-syd1:~# which az
/usr/bin/az
root@ubuntu-1cpu-1gb-au-syd1:~# az version
{
"azure-cli": "2.78.0",
"azure-cli-core": "2.78.0",
"azure-cli-telemetry": "1.1.0",
"extensions": {}
}
root@ubuntu-1cpu-1gb-au-syd1:~#
VNC
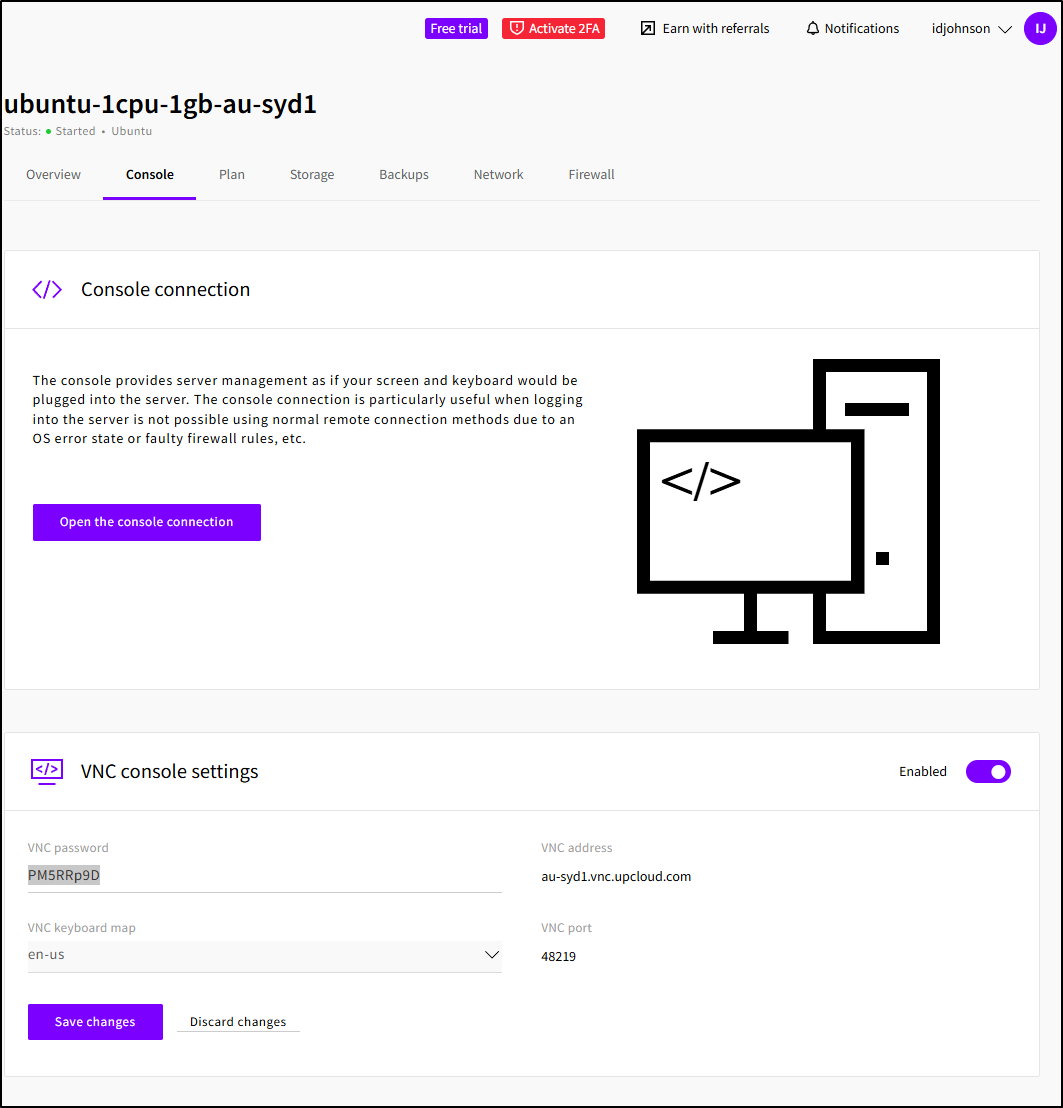
One interesting option with UpCloud is to enable a VNC console
I can then connect using something like RealVNC or similar
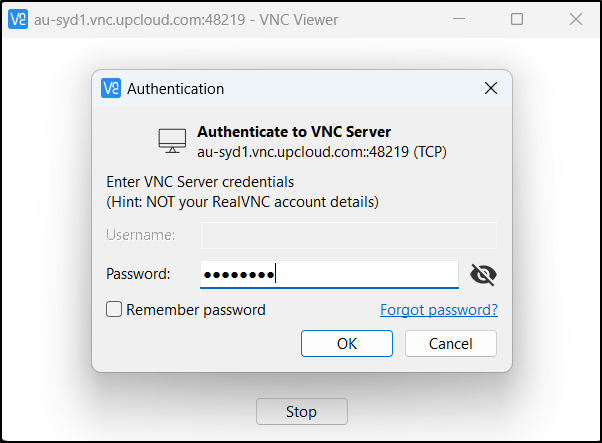
Use the password given
And then see the console
This would be more interesting with a graphical OS like Ubuntu Desktop or Windows but I have found such things useful when chasing server segfaults and crashes
Interestingly, when disabling, it did block new connections but left open my existing connection:
We can also hot resize some components in the console. For instance, I can easily increase the storage and memory:
Firewall
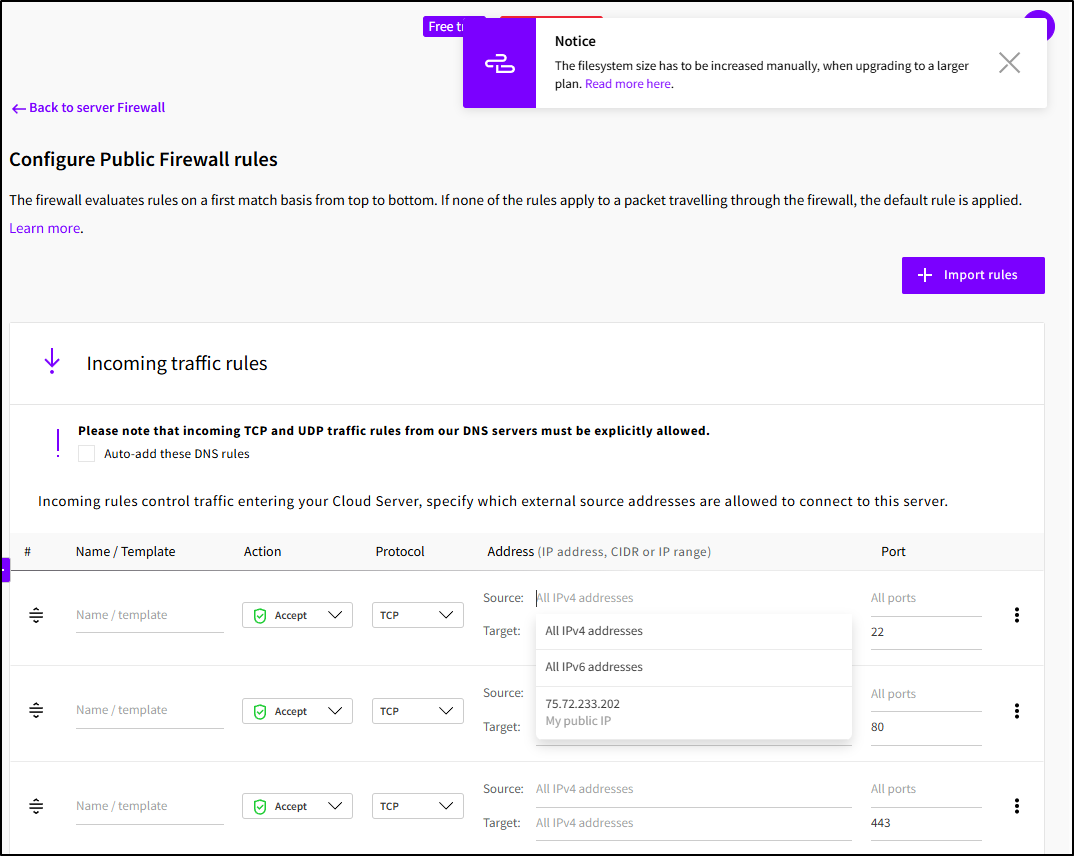
I wanted to restrict port 22 to just my egress IP which was prepopulated
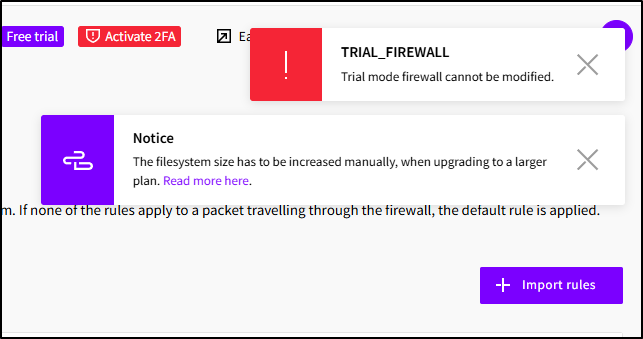
But when I went to save, I saw an error:
I think that is because I’m in the middle of a 7-day trial (and this would be modifiable if I were in a standard paid plan now).
We can use the console to delete servers just as easily as creating them:
Kubernetes
Let’s create our first Kubernetes Cluster now in UpCloud. We can see the “Create new cluster” option in the Kubernetes section
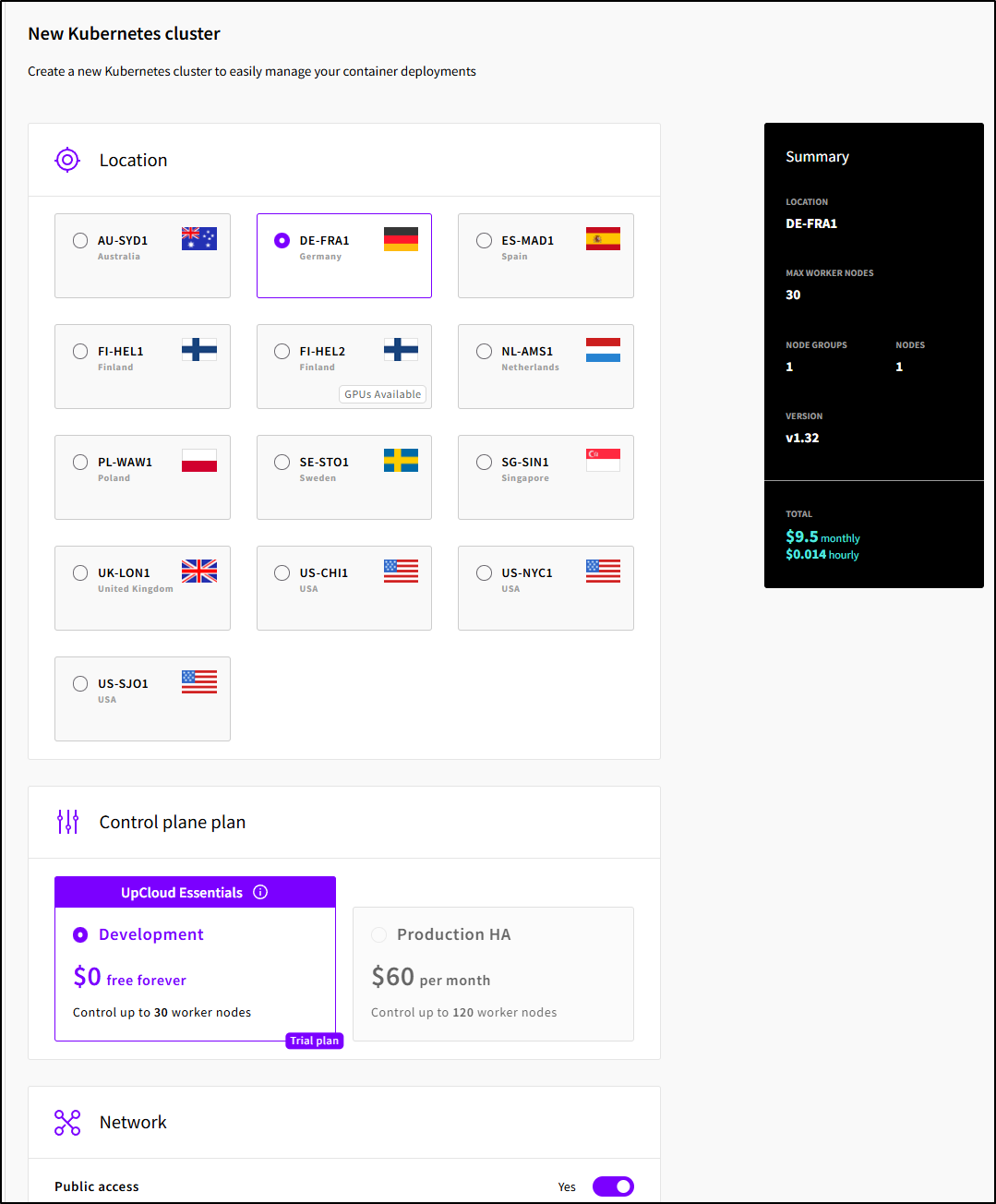
The basic plan has a free tier for the control plane. This does not mean our Nodes are free, just the control plane will be
I’m feeling zer gut so let’s create this one auf Deutschland.
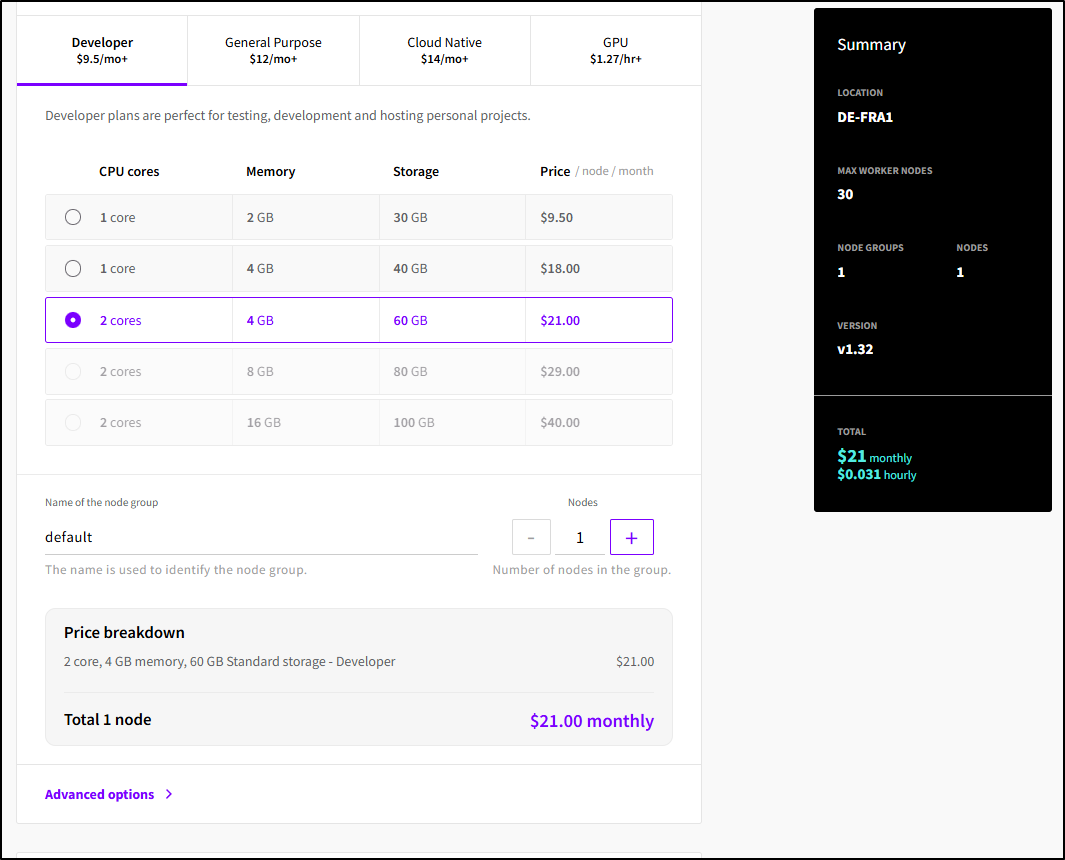
I saw the default was 1 node in the pool for 2Gb/20Gb storage (9.50 a month). Only the smallest workload would actually work in something that tiny. I’ll create a one node pool with a bit more memory and storage
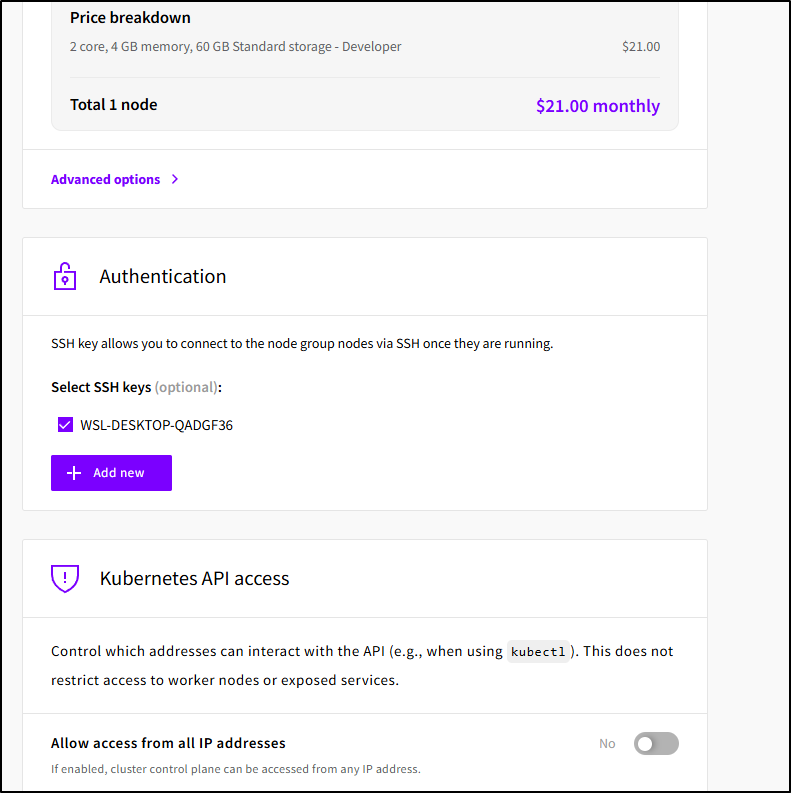
I rarely need to access my Node groups (unless I do something like front local storage with a GCP bucket using GSUtil or similar). But I did appreciate that I could pick an existing SSH key for admin break-glass access
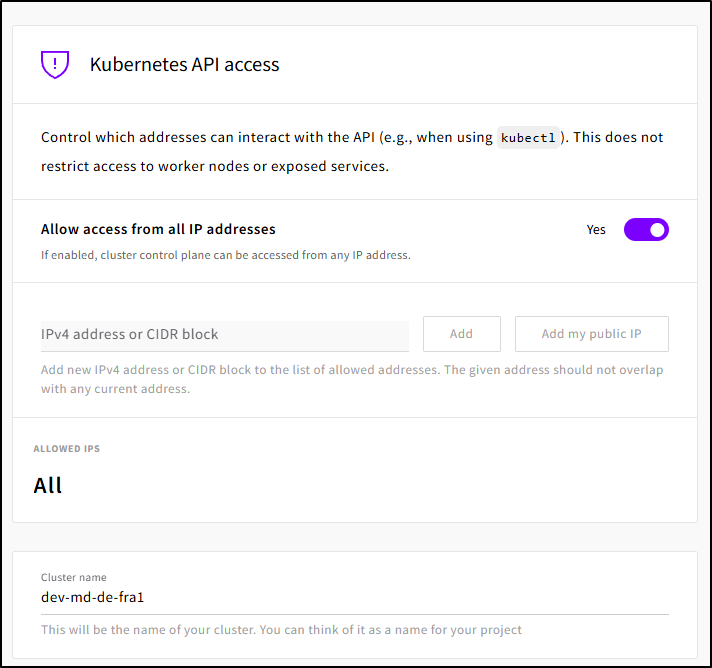
Some people like to restrict their API access. I tend to engage with K8s via ephemeral build agents from Github, Gitlab and the like. The default was off, but I enabled global access
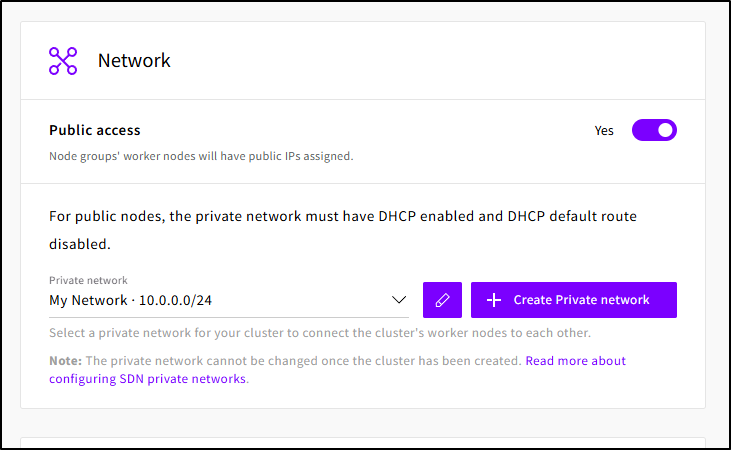
Before I could create, I did need to scroll back up and create at least one private network for the Node pool to use
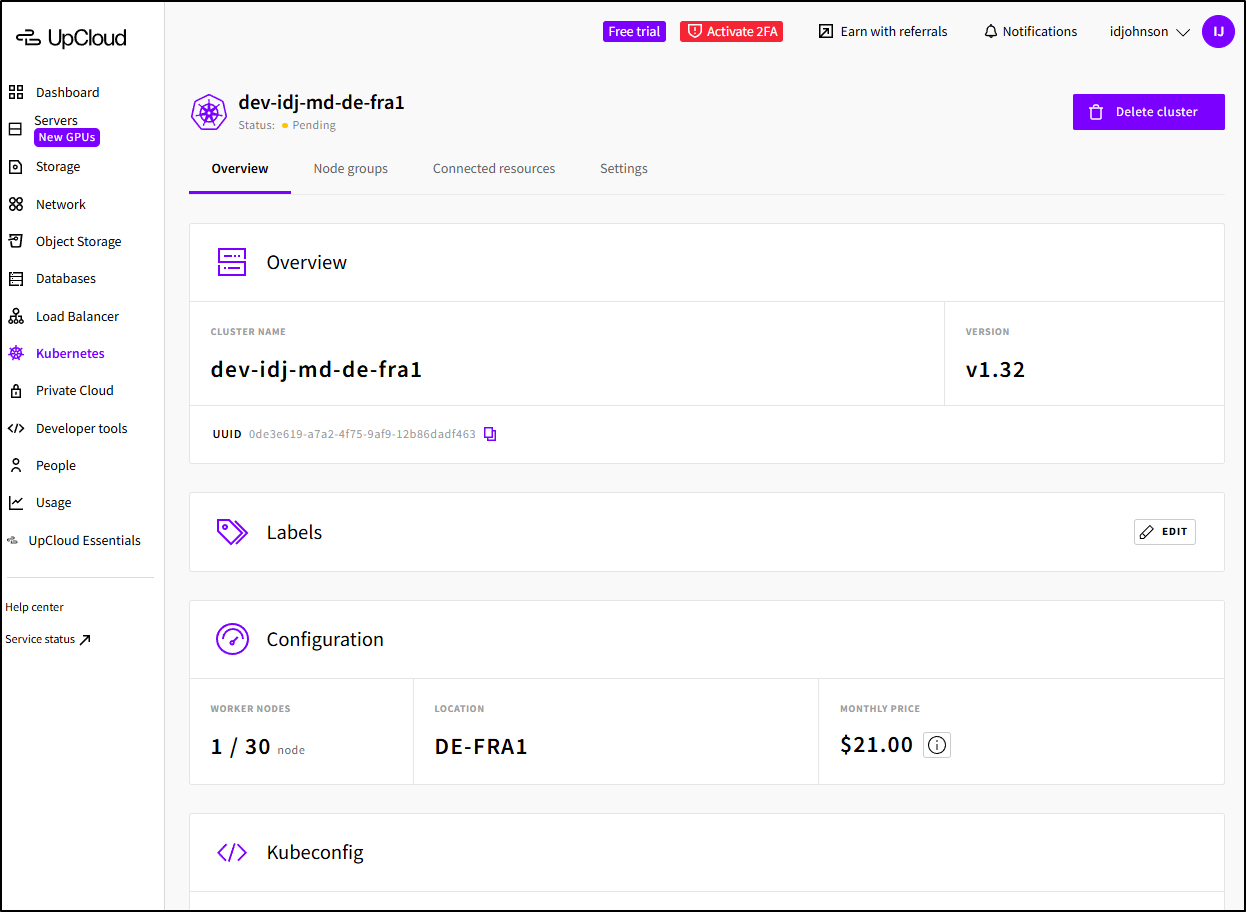
I could then “create cluster” and was taken to the cluster details page where I saw it was “Pending”
Let’s attempt to get the Kubeconfig
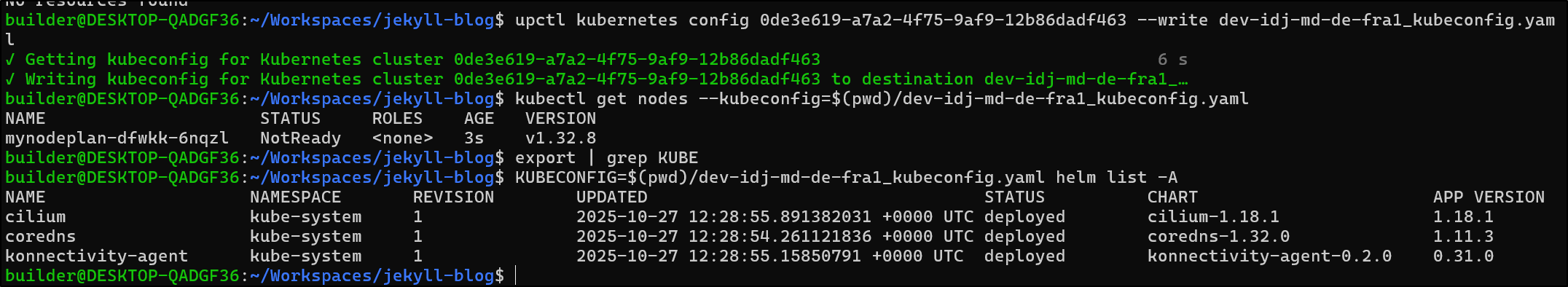
$ upctl kubernetes config 0de3e619-a7a2-4f75-9af9-12b86dadf463 --write dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
✓ Getting kubeconfig for Kubernetes cluster 0de3e619-a7a2-4f75-9af9-12b86dadf463 96 s
✓ Writing kubeconfig for Kubernetes cluster 0de3e619-a7a2-4f75-9af9-12b86dadf463 to destination dev-idj-md-de-fra1_ku…
However, I found it odd I saw no nodes
$ kubectl get nodes --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
No resources found
I think that was caused because I ran the command while it was still “Pending”. I ran it again when the cluster said “Running” and it worked
$ kubectl get nodes --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
mynodeplan-dfwkk-6nqzl NotReady <none> 3s v1.32.8
I can see some helm charts deployed already
Let’s do a test with a basic NGinx helm chart
$ KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml helm install my-release oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/nginx
Pulled: registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/nginx:22.2.1
Digest: sha256:449e1b8f6b5fffc44a1594ab439a12b18bd0730fe2aa5b19c155bb724b87a644
NAME: my-release
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Oct 27 07:34:33 2025
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: nginx
CHART VERSION: 22.2.1
APP VERSION: 1.29.2
⚠ WARNING: Since August 28th, 2025, only a limited subset of images/charts are available for free.
Subscribe to Bitnami Secure Images to receive continued support and security updates.
More info at https://bitnami.com and https://github.com/bitnami/containers/issues/83267
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
NGINX can be accessed through the following DNS name from within your cluster:
my-release-nginx.default.svc.cluster.local (port 80)
To access NGINX from outside the cluster, follow the steps below:
1. Get the NGINX URL by running these commands:
NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
Watch the status with: 'kubectl get svc --namespace default -w my-release-nginx'
export SERVICE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].port}" services my-release-nginx)
export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace default my-release-nginx -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
echo "http://${SERVICE_IP}:${SERVICE_PORT}"
WARNING: Rolling tag detected (bitnami/nginx:latest), please note that it is strongly recommended to avoid using rolling tags in a production environment.
+info https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-tanzu/application-catalog/tanzu-application-catalog/services/tac-doc/apps-tutorials-understand-rolling-tags-containers-index.html
WARNING: Rolling tag detected (bitnami/git:latest), please note that it is strongly recommended to avoid using rolling tags in a production environment.
+info https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-tanzu/application-catalog/tanzu-application-catalog/services/tac-doc/apps-tutorials-understand-rolling-tags-containers-index.html
WARNING: Rolling tag detected (bitnami/nginx-exporter:latest), please note that it is strongly recommended to avoid using rolling tags in a production environment.
+info https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-tanzu/application-catalog/tanzu-application-catalog/services/tac-doc/apps-tutorials-understand-rolling-tags-containers-index.html
WARNING: There are "resources" sections in the chart not set. Using "resourcesPreset" is not recommended for production. For production installations, please set the following values according to your workload needs:
- cloneStaticSiteFromGit.gitSync.resources
- resources
+info https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
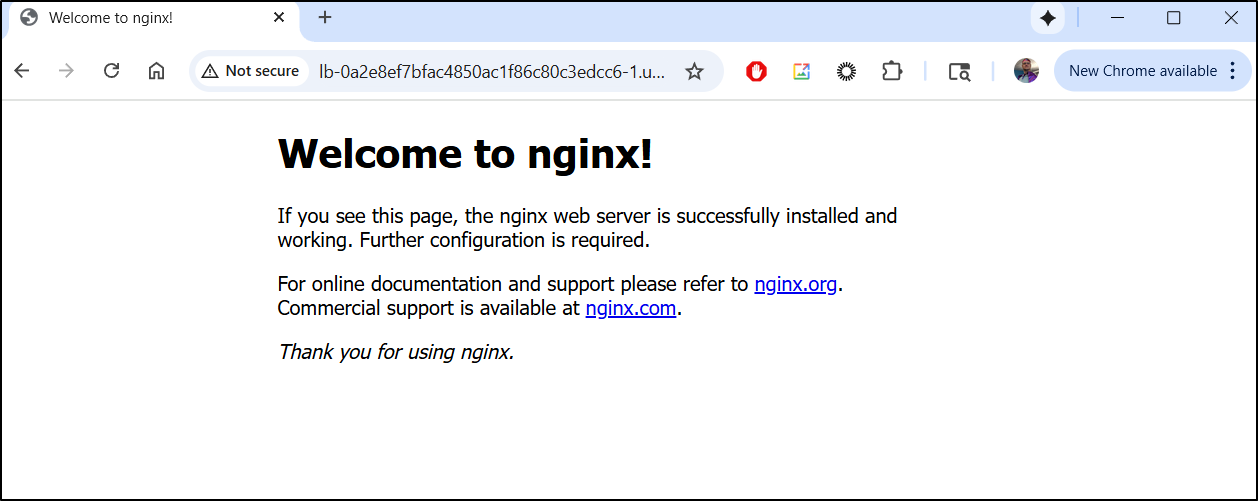
I can see it running now
$ kubectl get po --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-release-nginx-b4dbcfccc-mgjsh 1/1 Running 0 5m59s
While my local WSL seemed to fail on the port-forward, I did look up the LB which was granted
builder@DESKTOP-QADGF36:~/Workspaces/jekyll-blog$ kubectl port-forward my-release-nginx-b4dbcfccc-mgjsh --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml 8080:80
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 80
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 80
Handling connection for 8080
Handling connection for 8080
E1027 07:41:37.837932 49102 portforward.go:424] "Unhandled Error" err="an error occurred forwarding 8080 -> 80: error forwarding port 80 to pod 29ce20d19df07098212b18c83557af10456946f35ef4f5b9f92bda5b327b277e, uid : failed to execute portforward in network namespace \"/var/run/netns/cni-5e4bcfb4-b41c-469a-50a2-46aa27856d66\": failed to connect to localhost:80 inside namespace \"29ce20d19df07098212b18c83557af10456946f35ef4f5b9f92bda5b327b277e\", IPv4: dial tcp4 127.0.0.1:80: connect: connection refused IPv6 dial tcp6 [::1]:80: connect: connection refused "
error: lost connection to pod
builder@DESKTOP-QADGF36:~/Workspaces/jekyll-blog$ kubectl get --namespace default -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].port}" services my-release-nginx --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
80builder@DESKTOP-QADGF36:~/Workspaces/jekyll-blog$ kubectl get svc --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml 8080:80
Error from server (NotFound): services "8080:80" not found
builder@DESKTOP-QADGF36:~/Workspaces/jekyll-blog$ kubectl get svc --kubeconfig=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 13m
my-release-nginx LoadBalancer 10.96.26.154 lb-0a2e8ef7bfac4850ac1f86c80c3edcc6-1.upcloudlb.com 80:31889/TCP,443:31536/TCP 7m49s
and that came up without issue
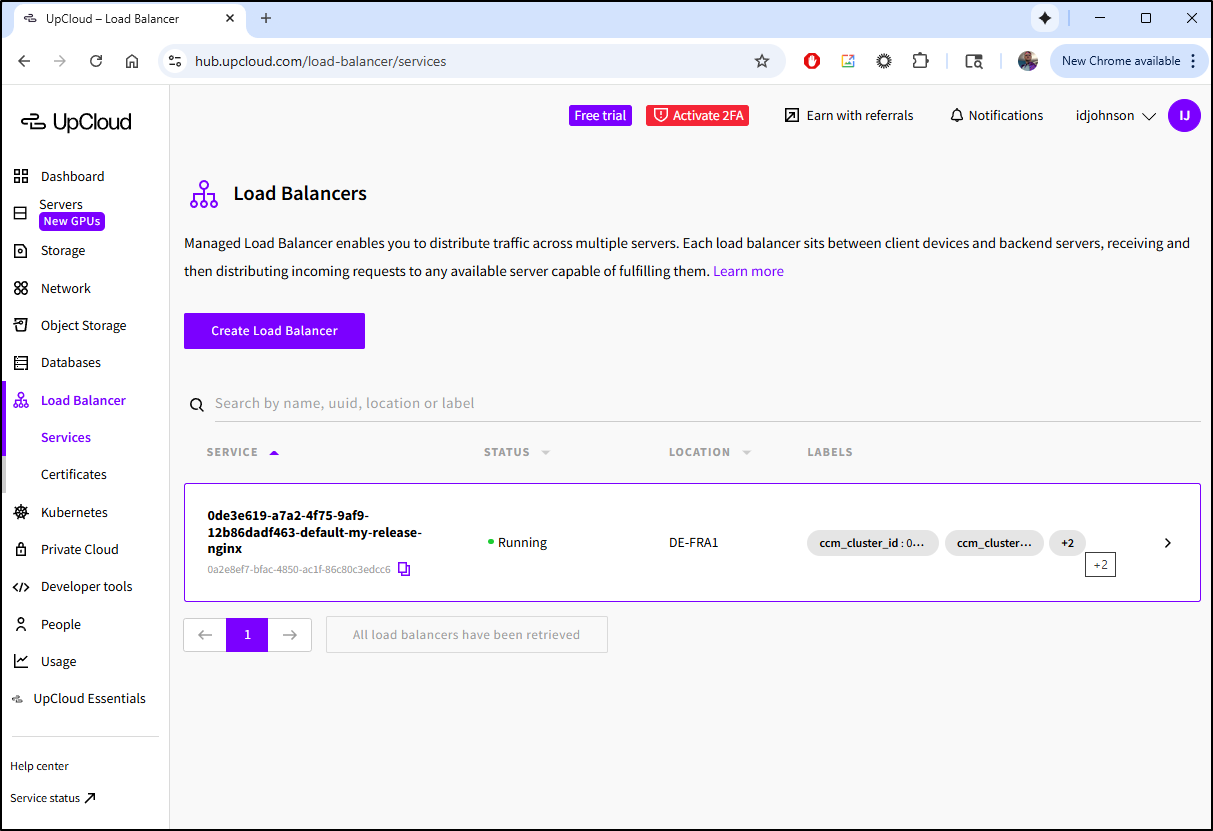
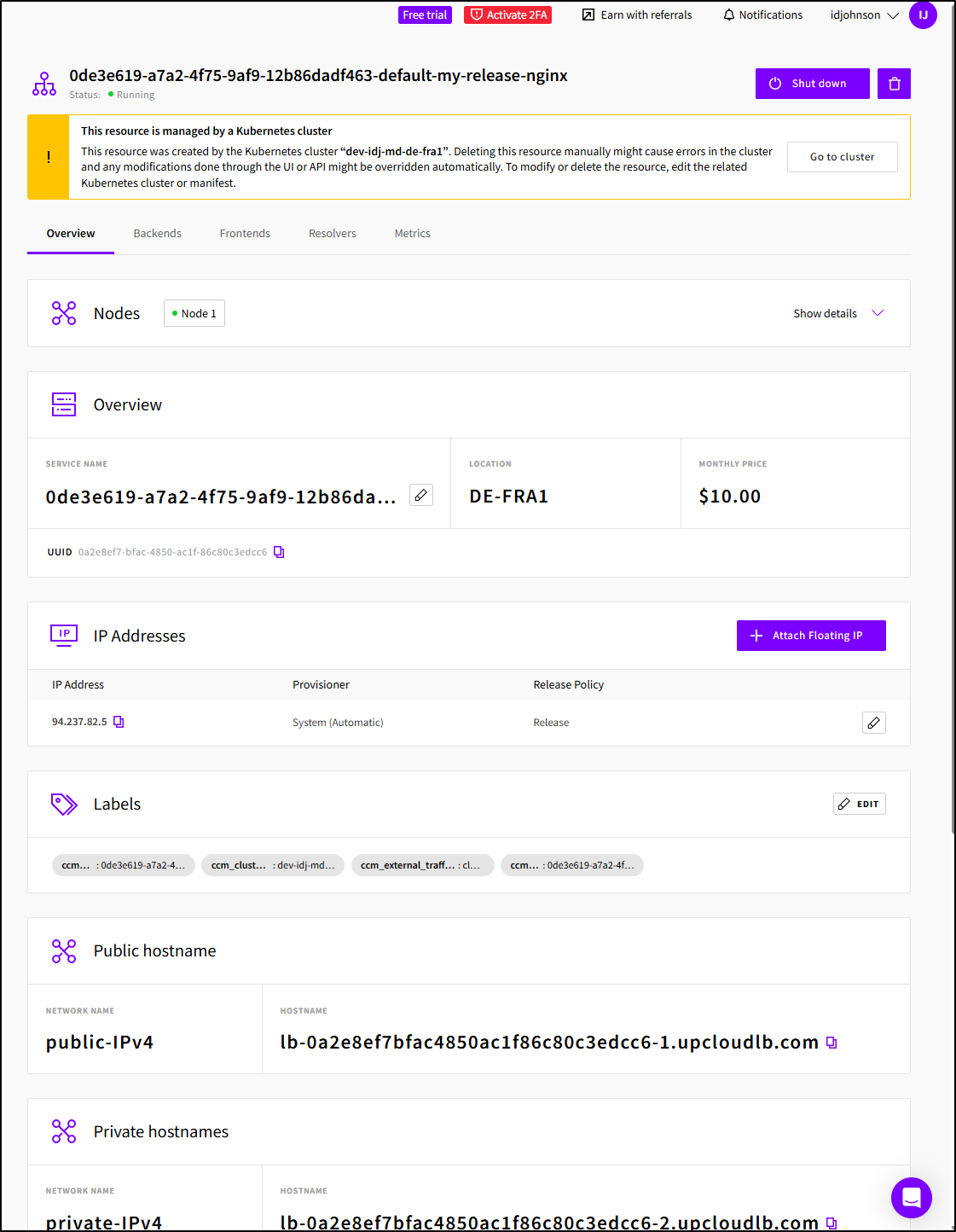
I can also see that LoadBalancer created in the Hub
The details of which note it was created in the cluster
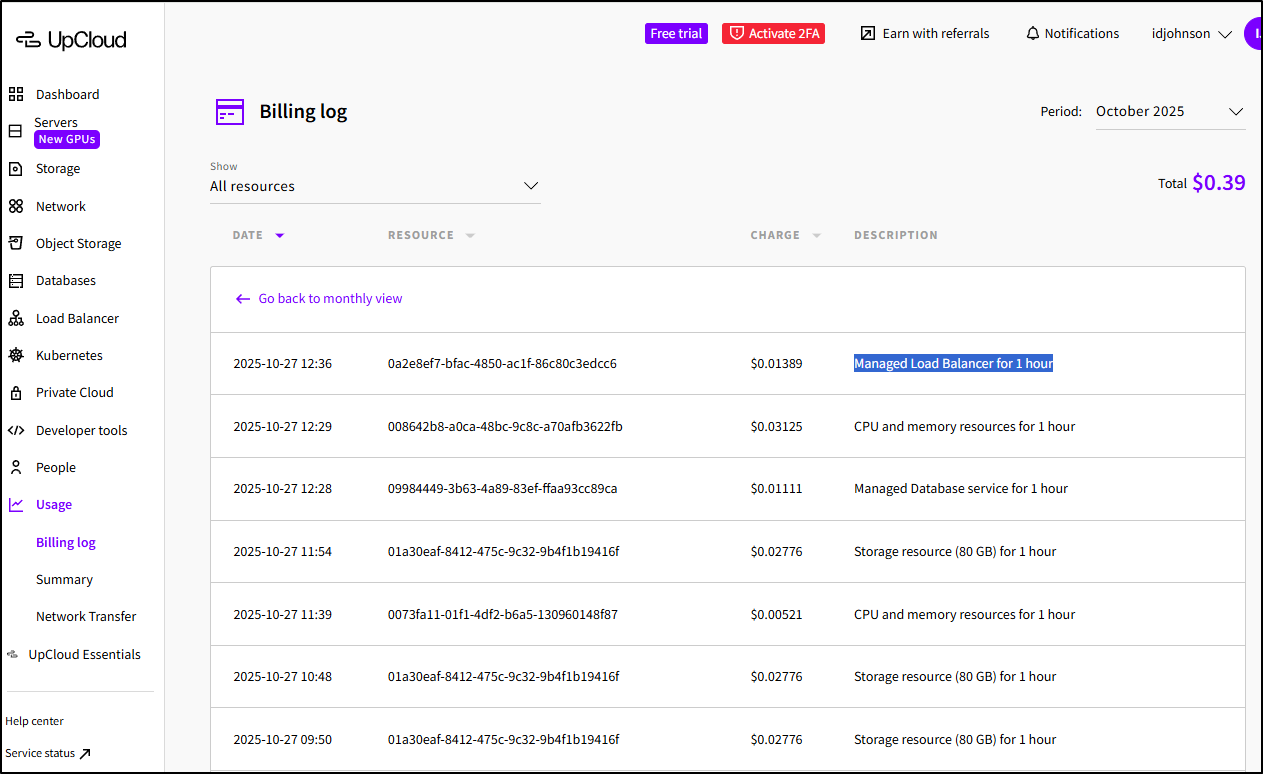
This is an important note: The public IP’ed load balancer which was created by helm will cost me US$10 a month on top of my K8s bills. So be aware of things like PVCs and LBs that can add to your cloud costs
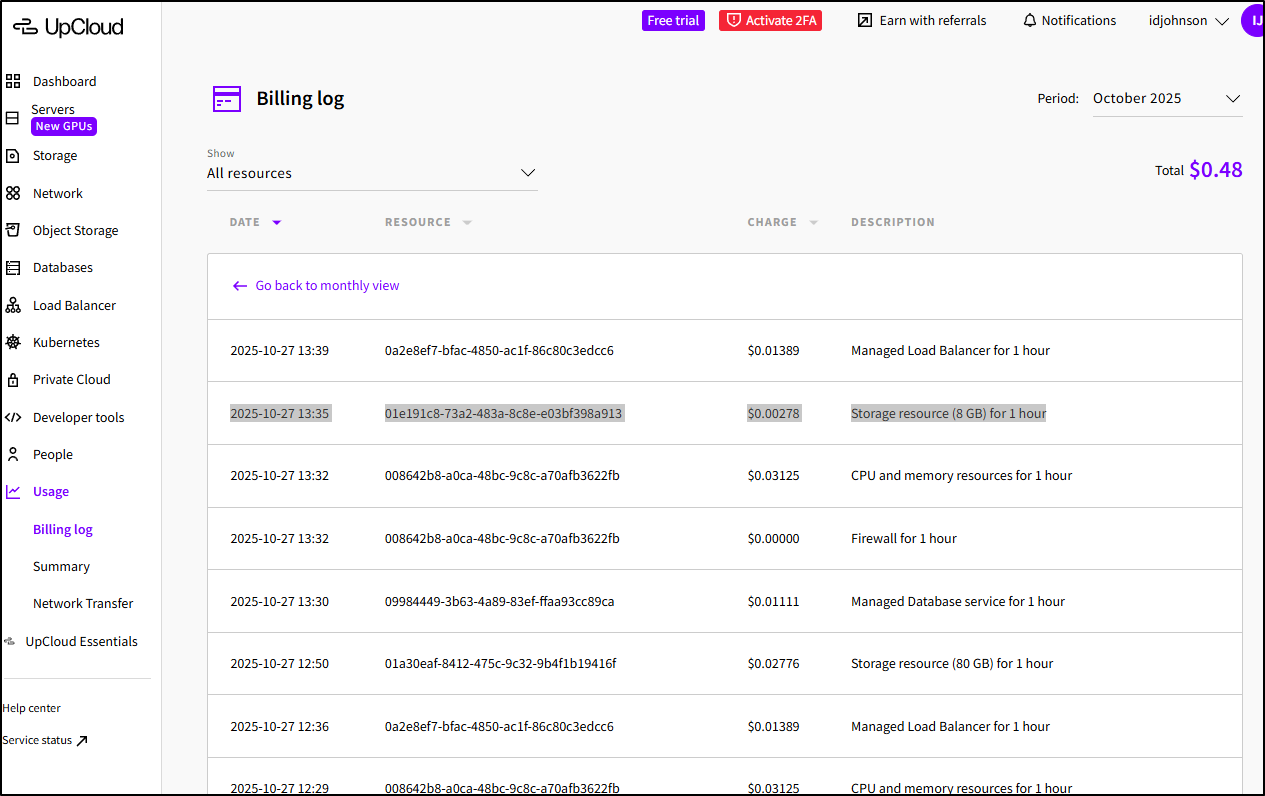
Another way to see that is in the Billing Log
Let’s fire up a PostgreSQL instance in K8s as well - this should show PVCs
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
"bitnami" already exists with the same configuration, skipping
$ KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/dev-idj-md-de-fra1_kubeconfig.yaml helm install
my-psql-release bitnami/postgresql
NAME: my-psql-release
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Oct 27 08:35:33 2025
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: postgresql
CHART VERSION: 16.7.27
APP VERSION: 17.6.0
⚠ WARNING: Since August 28th, 2025, only a limited subset of images/charts are available for free.
Subscribe to Bitnami Secure Images to receive continued support and security updates.
More info at https://bitnami.com and https://github.com/bitnami/containers/issues/83267
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
PostgreSQL can be accessed via port 5432 on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
my-psql-release-postgresql.default.svc.cluster.local - Read/Write connection
To get the password for "postgres" run:
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace default my-psql-release-postgresql -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password}" | base64 -d)
To connect to your database run the following command:
kubectl run my-psql-release-postgresql-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --namespace default --image docker.io/bitnami/postgresql:17.6.0-debian-12-r4 --env="PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" \
--command -- psql --host my-psql-release-postgresql -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
> NOTE: If you access the container using bash, make sure that you execute "/opt/bitnami/scripts/postgresql/entrypoint.sh /bin/bash" in order to avoid the error "psql: local user with ID 1001} does not exist"
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl port-forward --namespace default svc/my-psql-release-postgresql 5432:5432 &
PGPASSWORD="$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" psql --host 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
WARNING: The configured password will be ignored on new installation in case when previous PostgreSQL release was deleted through the helm command. In that case, old PVC will have an old password, and setting it through helm won't take effect. Deleting persistent volumes (PVs) will solve the issue.
WARNING: There are "resources" sections in the chart not set. Using "resourcesPreset" is not recommended for production. For production installations, please set the following values according to your workload needs:
- primary.resources
- readReplicas.resources
+info https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/
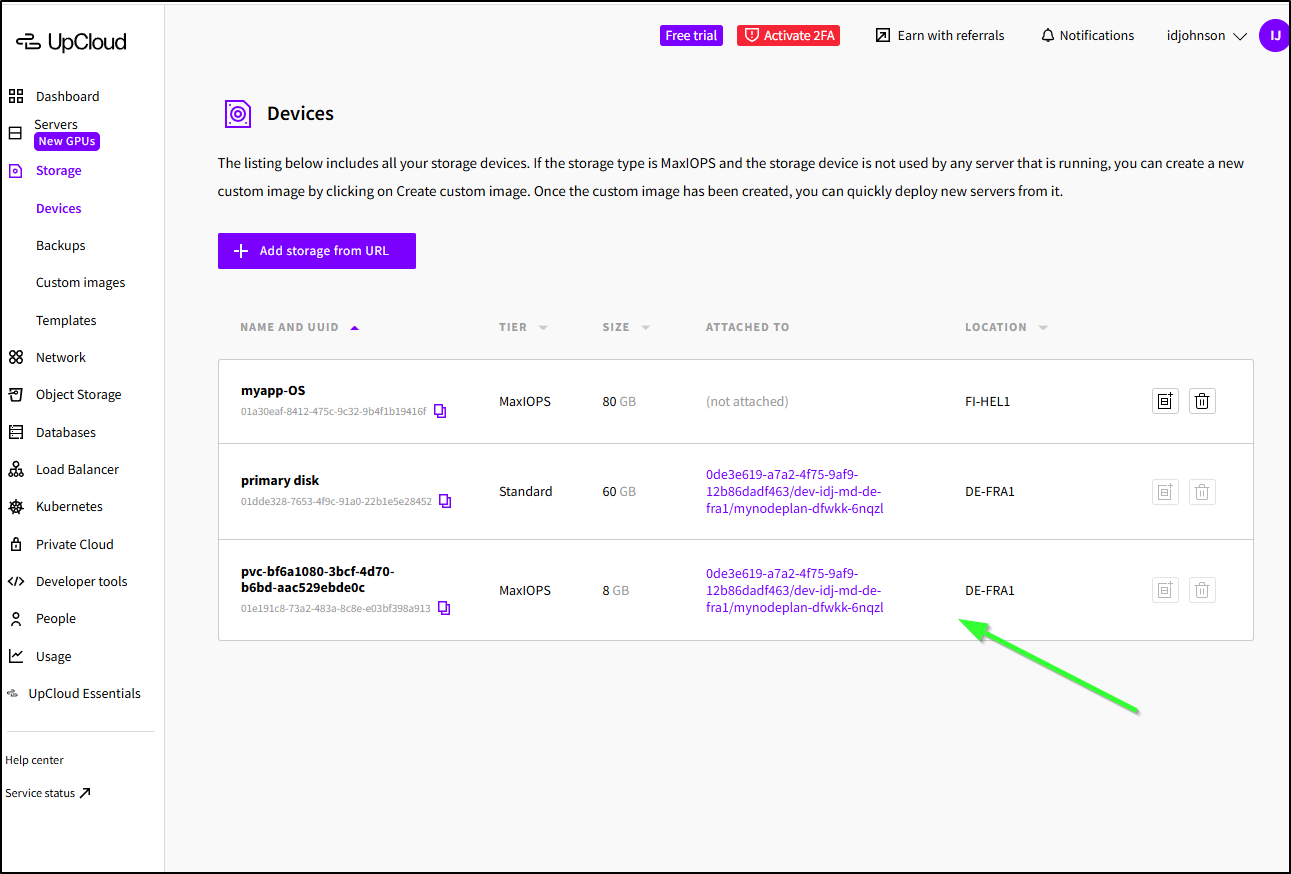
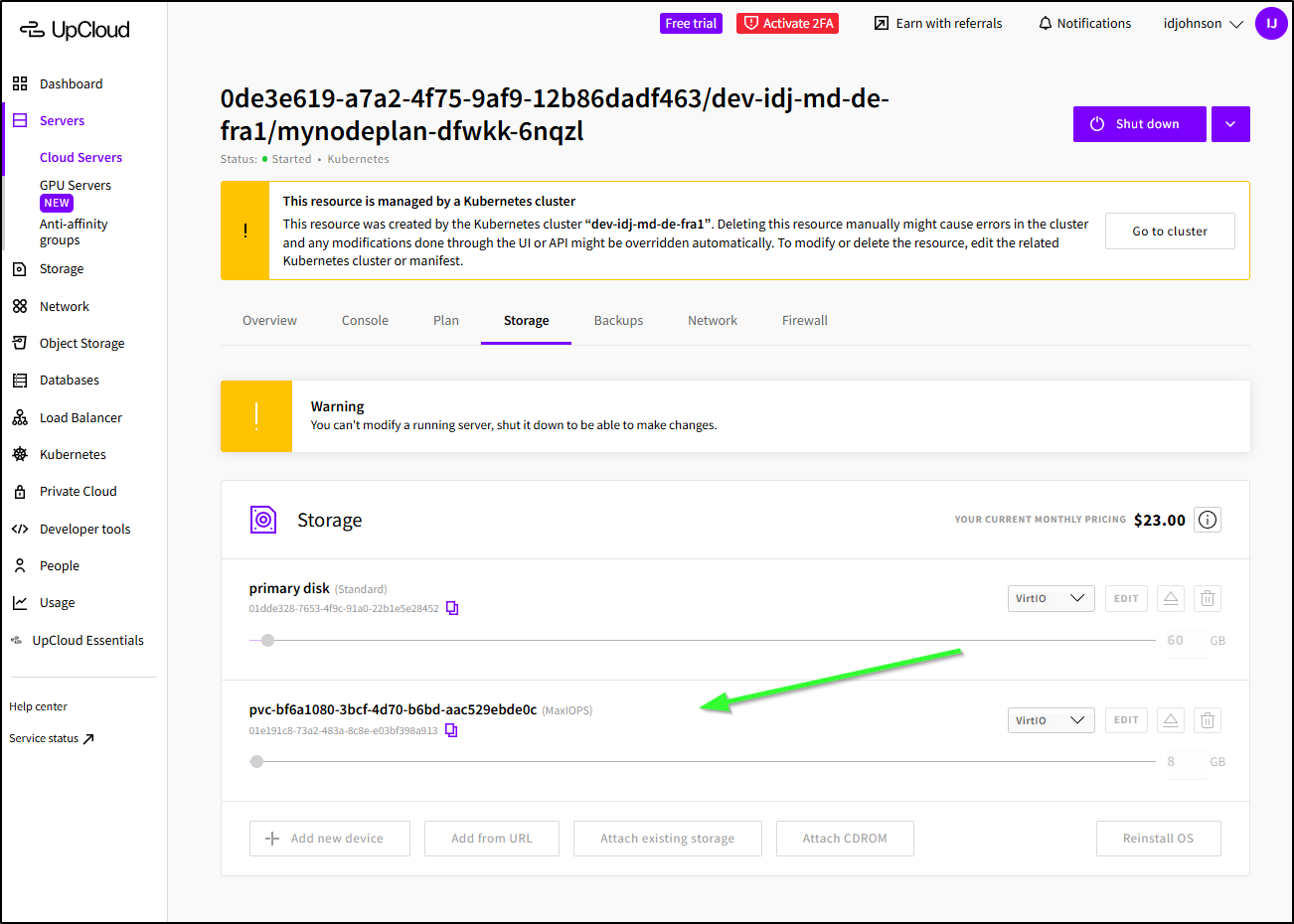
The PVC will not be in object storage (that is more akin to a GCP Bucket or AWS S3 bucket), however it will be in Storage under servers
Note: this is not billed like a separate storage volume as we would see in other clouds, we’ll see it tagged onto the Server instance in the Storage tab instead
That said, I do see it as a line item in the billing
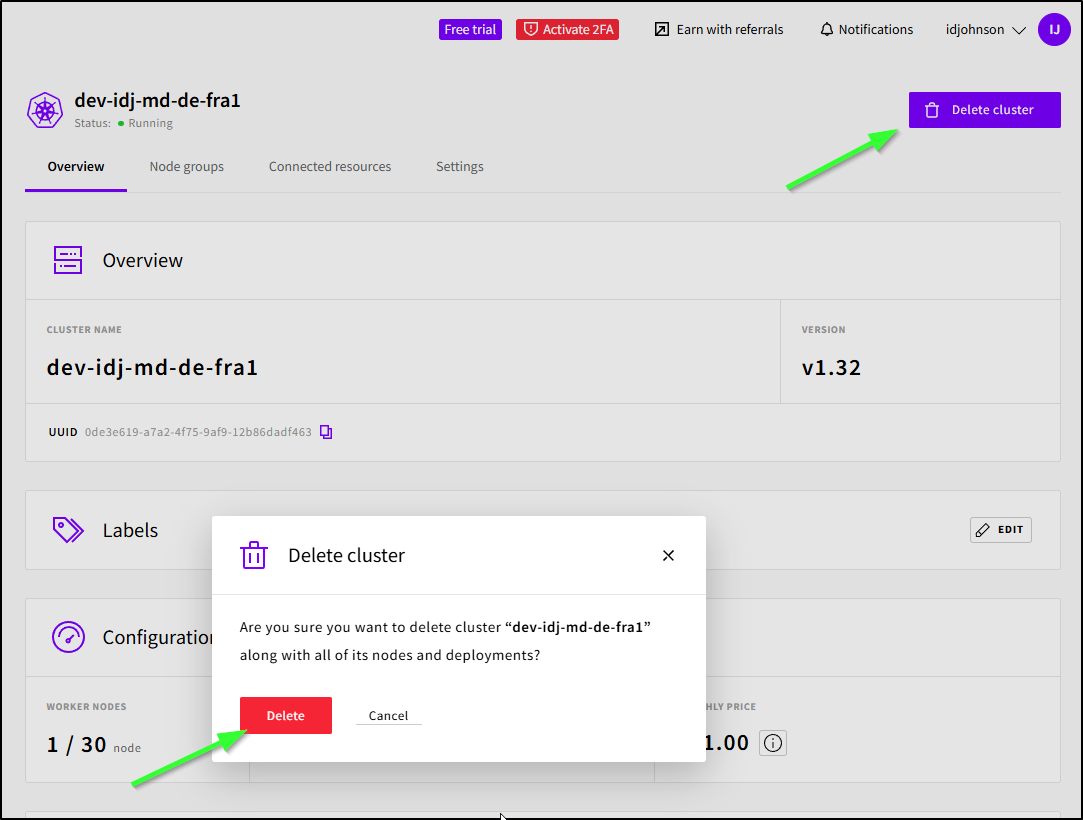
Let’s see what is cleaned up when we delete a cluster
I get a pop-up saying cluster deletion has started
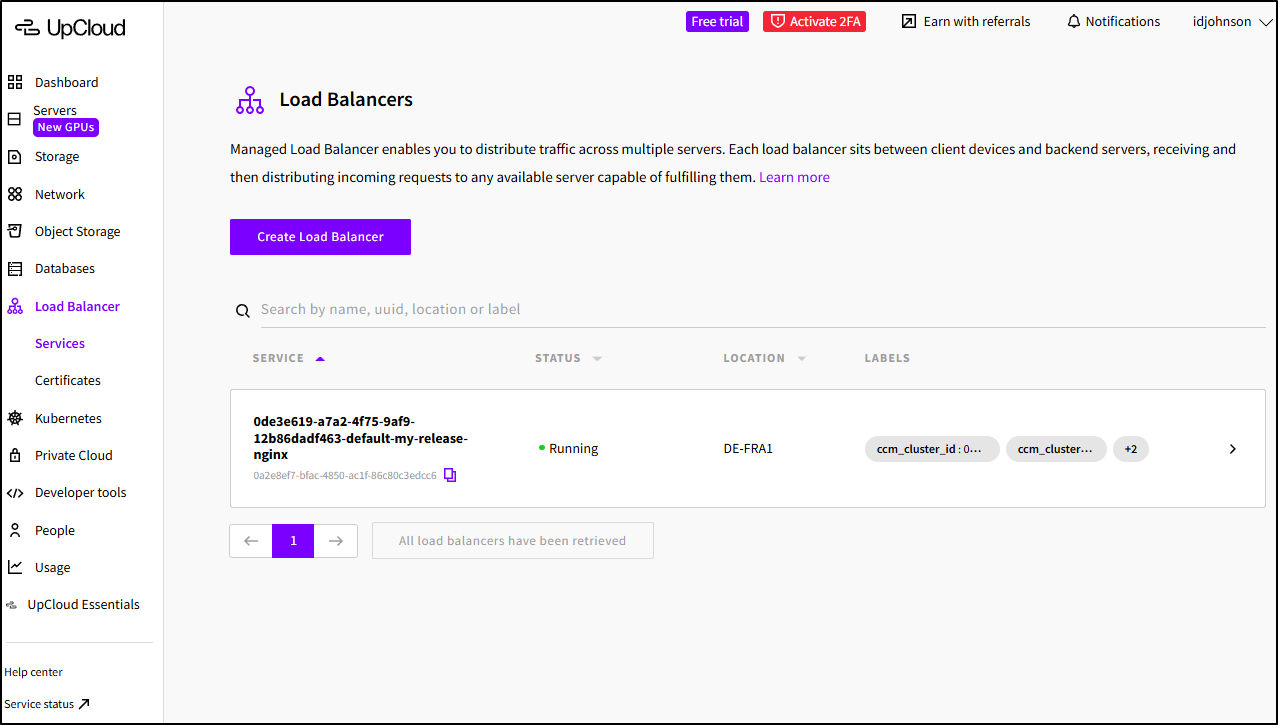
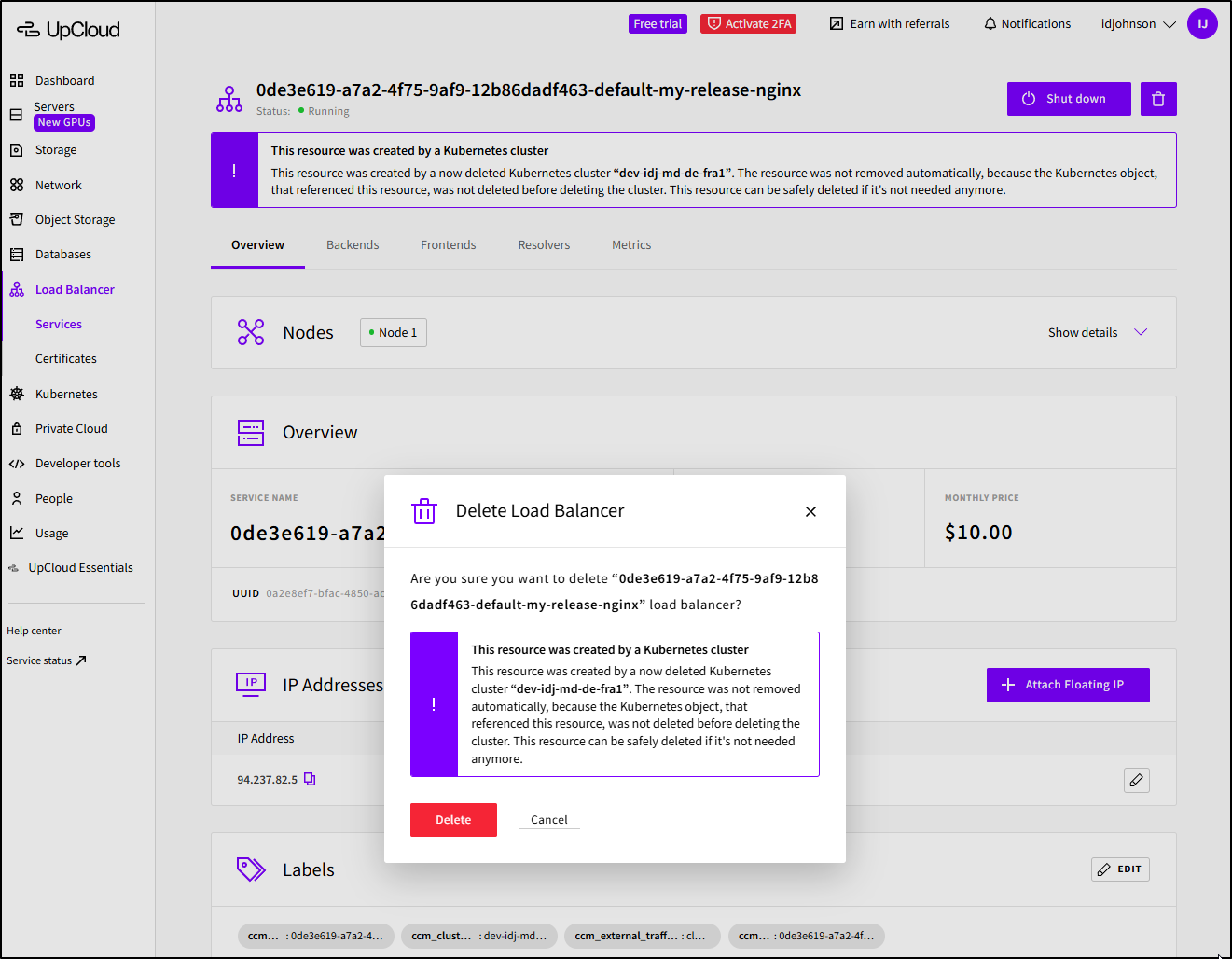
Later in the day I checked back on the Load Balancers - was the Nginx one deleted?
Indeed it was not and I needed to delete it by hand
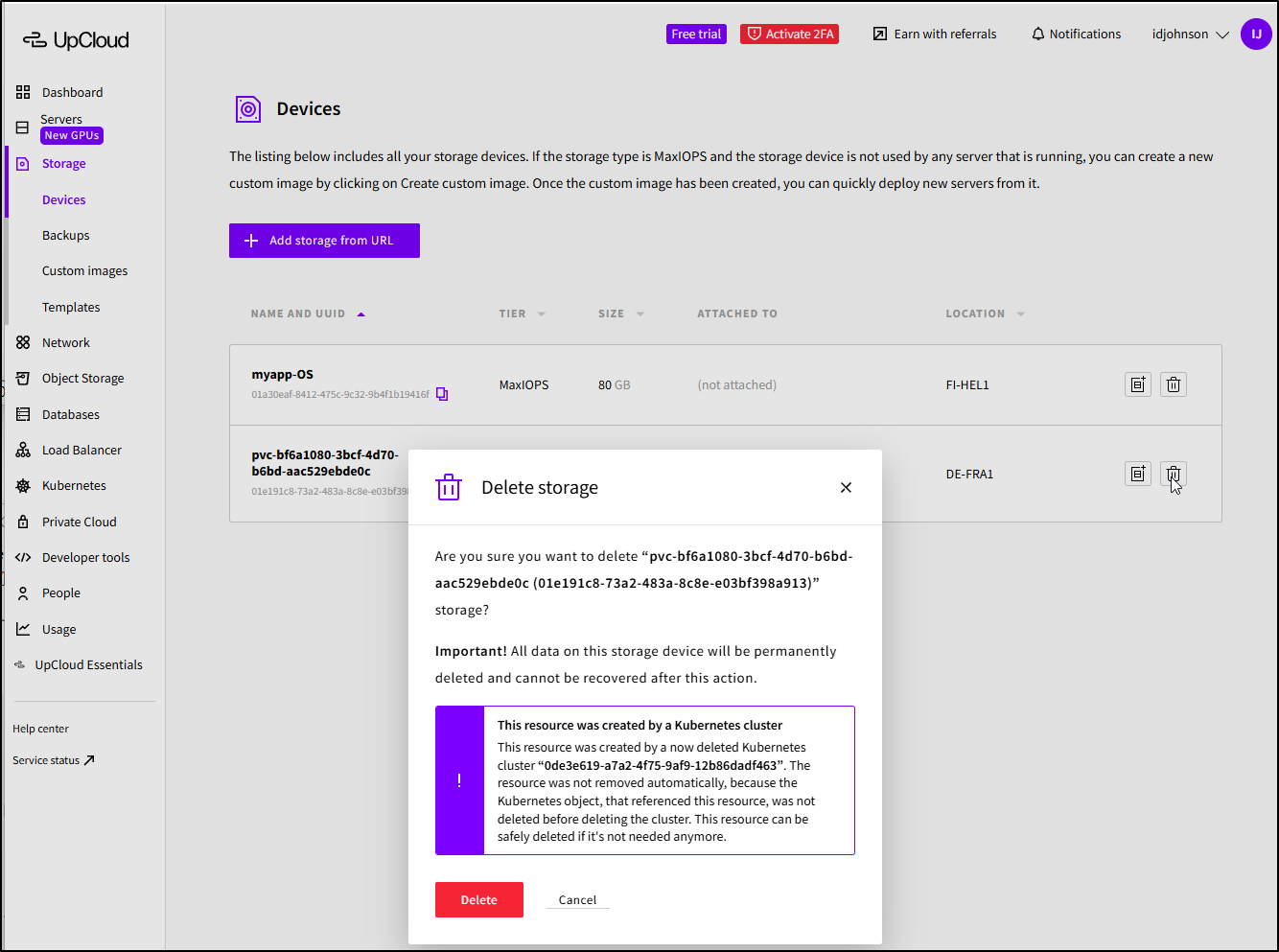
The PVC was also left in place and needed to be removed
This is not a deficiency, mind you. Many clouds do the same. Sometimes people want to review the PVC or attach it elsewhere, or get the backup data off it. It is a good policy to, by default, leave Volumes. Additionally, one may have traffic routing into a Cluster via the LB and you want to redirect it seamlessly elsewhere - once could just adjust the backend to make that happen and not worry that the cluster removal will delete the LB.
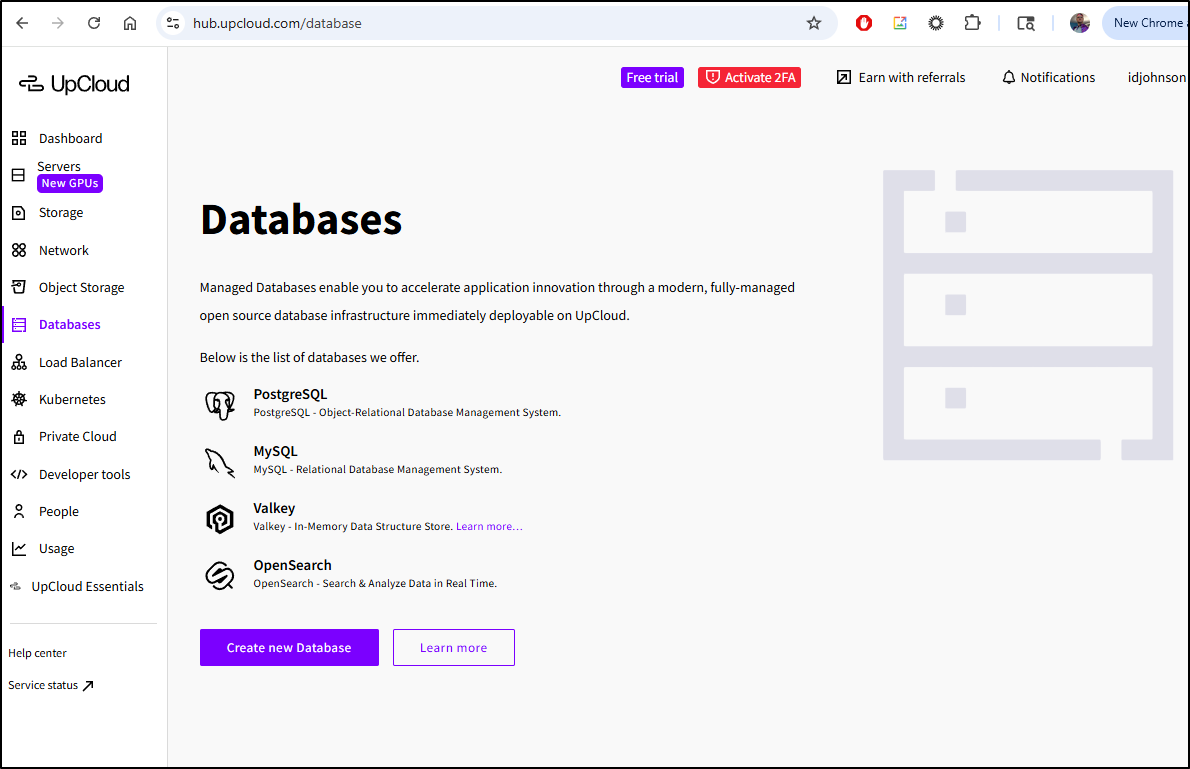
Databases
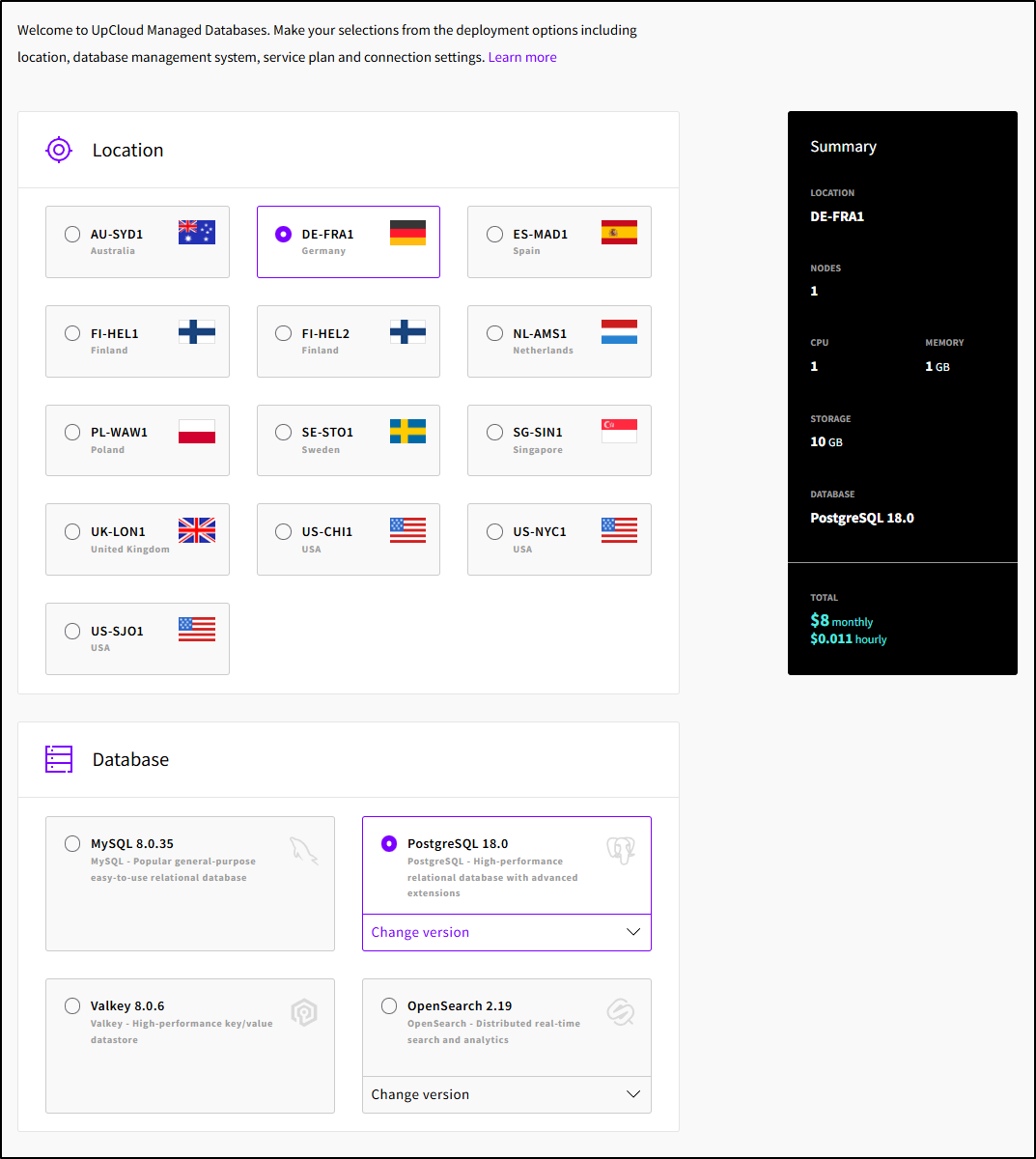
We can create a new database from the Databases page in the Hub.
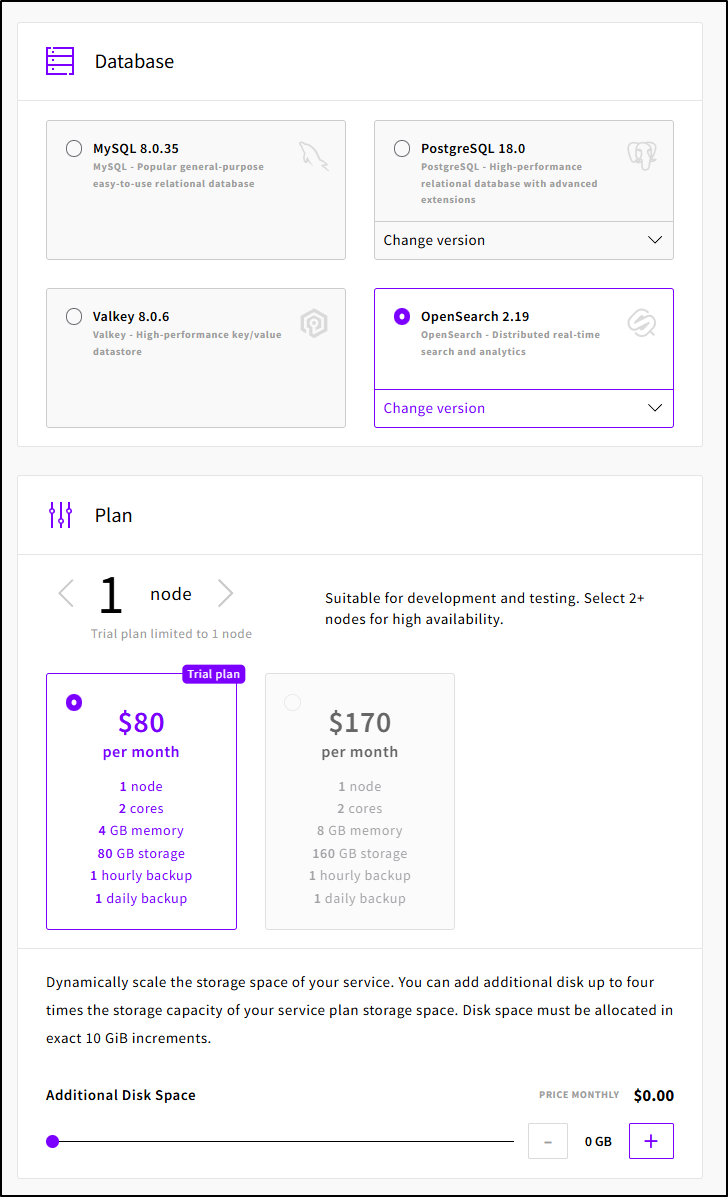
I have a few regions and Database types from which to pick
The all have a plan that starts at US$8 a month except for OpenSearch which starts at $80
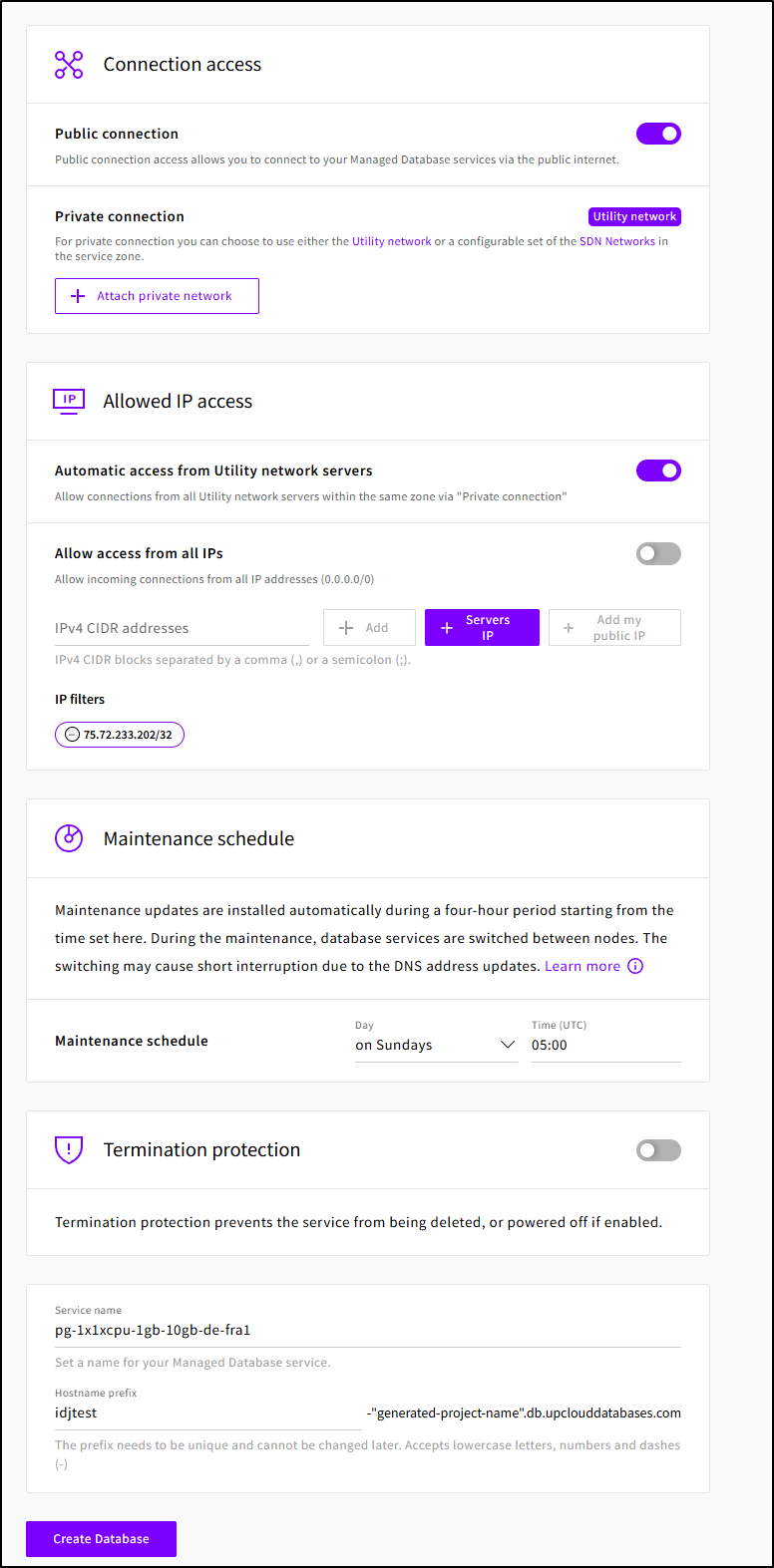
While I will let it have a Public IP, I’ll restrict access to just my egress IP for now
When I click create, I can see it going through the setup statuses
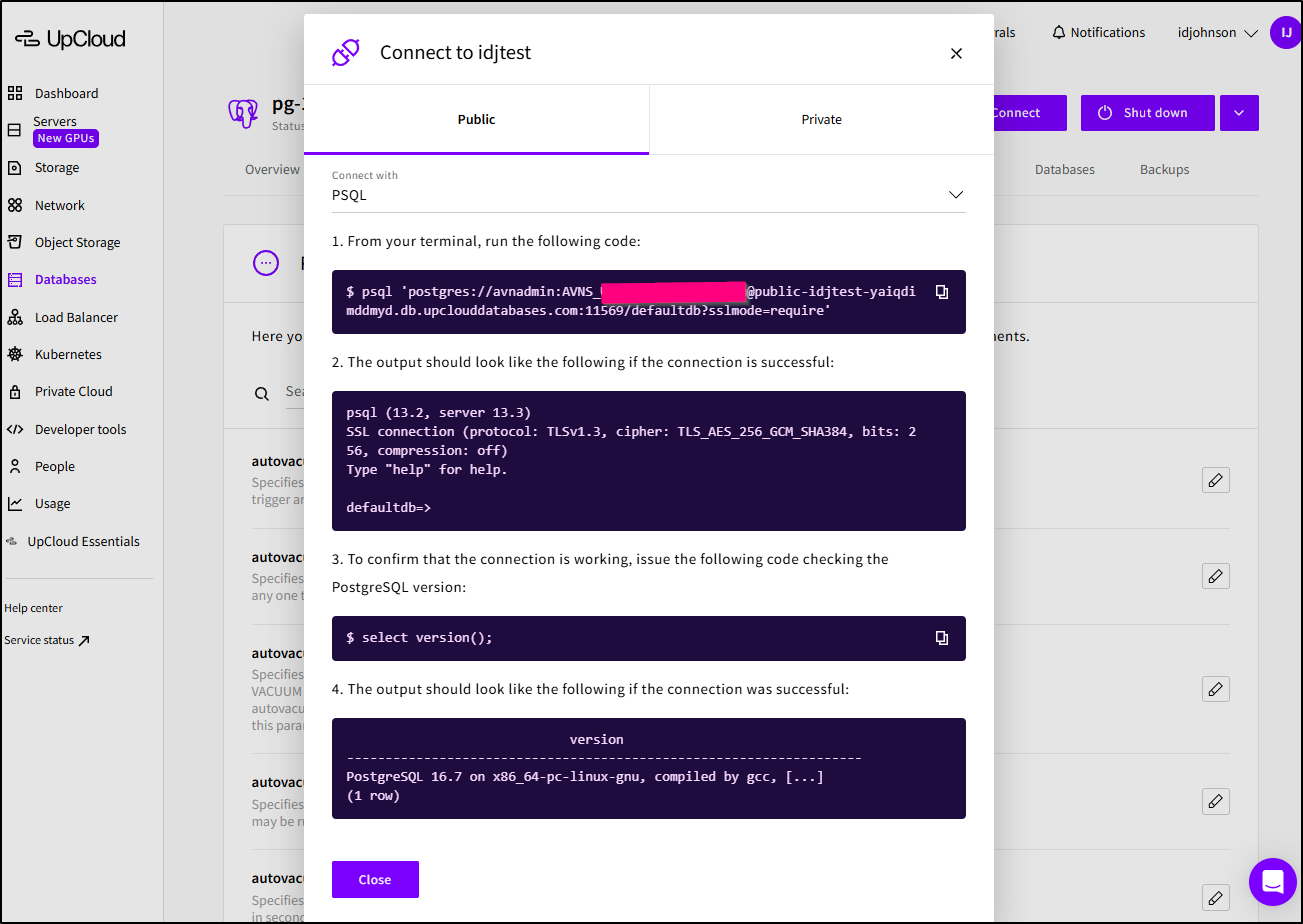
I can use the connection string (which is also shown in the “connect”) page
To connect to and configure the database
$ psql 'postgres://avnadmin:asdfasfasdfsadf@public-idjtest-yaiqdimddmyd.db.upclouddatabases.com:11569/defaultdb?sslmode=require'
psql (14.19 (Ubuntu 14.19-0ubuntu0.22.04.1), server 18.0)
WARNING: psql major version 14, server major version 18.
Some psql features might not work.
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
defaultdb=> select version();
version
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PostgreSQL 18.0 on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 14.2.1 20240912 (Red Hat 14.2.1-3), 64-bit
(1 row)
defaultdb=>
Cleanup
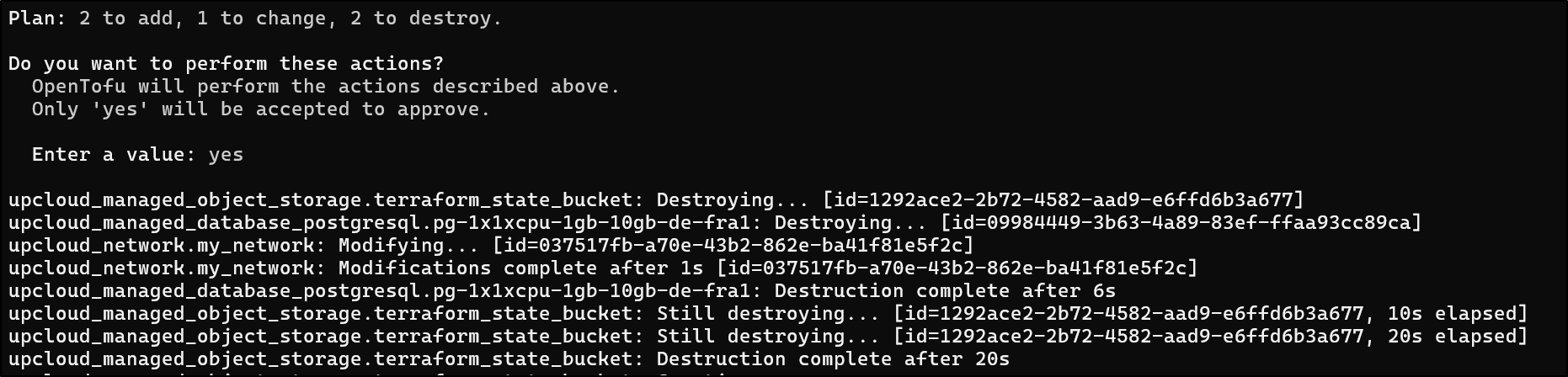
Since we have this imported into Terraform, I’m curious if just removing it will perform the shutdown and delete. I say this because in the UI, we cannot do delete until it’s been shutdown:
Indeed, the delete worked
And my database page was empty
Summary
In this post we started with UpCloud signup before moving on to using the CLI and Hub to create VMs. We explored SSH key nuances, the firewall setup and VNC usage for graphical interface interactions.
We then explored Kubernetes setup and costs before digging into Database Usage. I showed setting up and connecting to a PostgreSQL database before doing a cleanup. While my cleanup shows Terraform, you’ll have to wait till the next article where I really dig into the Terraform setup and usage (consider it a preview).
I’m really enjoying UpCloud so far so I recommend using my signup link – which if you end up liking it I might get some kind of cloud credit (if you don’t or cancel, I don’t get anything, but I’m not here to sell stuff - I just like free cloud spend when it’s an option)